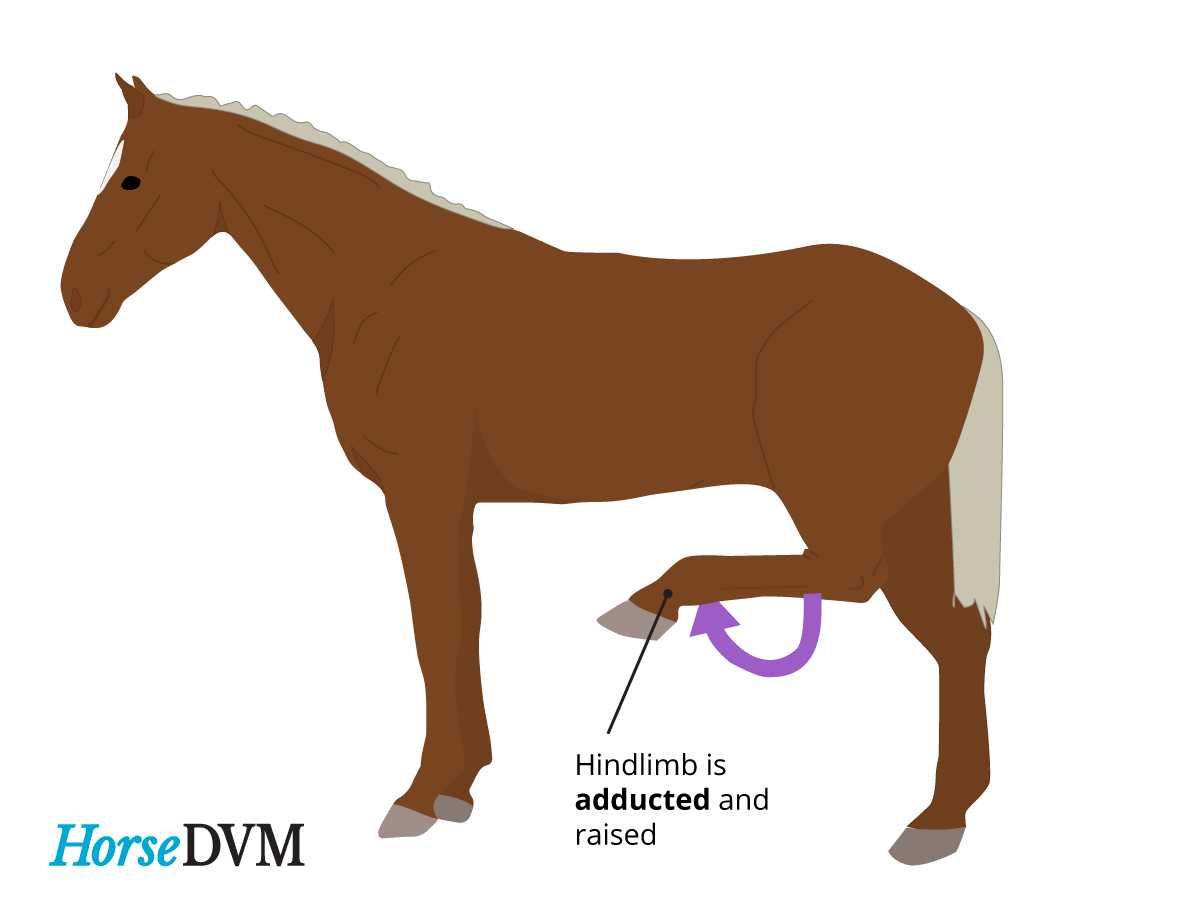
Stringhalt in horses is a neuromuscular disorder that affects the hind limbs, causing involuntary and exaggerated movements. It is characterized by sudden jerking or spasms when the horse moves, particularly when walking or trotting. This condition can be caused by various factors such as nerve damage, toxic plants, or metabolic imbalances. Stringhalt can significantly impact a horse’s movement and overall performance. Early detection and proper management are essential for alleviating discomfort and maintaining the horse’s quality of life.
Causes of Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses and is characterized by abnormal, exaggerated movements of the hind legs. It can cause the horse to excessively flex or jerk its hind limbs while walking or trotting. This can be a painful and frustrating condition for both the horse and its owner. Understanding the causes of stringhalt is crucial in order to effectively diagnose and treat the condition.
1. Toxic Plants
One of the primary causes of stringhalt in horses is the consumption of toxic plants. Certain plants contain toxins that can affect the nervous system of the horse, leading to muscle spasms and abnormal movements. Plants such as flatweed, white snakeroot, and rayless goldenrod have been associated with stringhalt in horses.
2. Nerve Damage
In some cases, nerve damage can be responsible for stringhalt. Trauma to the nerves in the hind legs, such as from an injury, can disrupt the normal functioning of the nerves and result in the development of stringhalt. Nerve damage can also occur due to the compression of nerves by tumors or abnormal growths.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
Poor nutrition can contribute to the development of stringhalt in horses. A lack of essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin E or selenium, can lead to muscle dysfunction and abnormal movements. It is important to ensure that horses receive a balanced diet to prevent nutritional deficiencies.
4. Hereditary Factors
Stringhalt can also have a hereditary component. Some horses may be genetically predisposed to developing this condition, and it can be passed down from one generation to another. In these cases, proper breeding practices and genetic testing can help reduce the risk of stringhalt.
5. Miscellaneous Causes
There are other less common causes of stringhalt in horses. These can include infections, such as tetanus or Lyme disease, which can affect the nervous system and lead to abnormal muscle movements. In some cases, certain medications or toxins can also trigger stringhalt.
Summary
Stringhalt in horses is a condition characterized by abnormal movements of the hind legs. It can be caused by various factors such as the consumption of toxic plants, nerve damage, nutritional deficiencies, hereditary factors, infections, and medications. Understanding the causes of stringhalt is essential in order to provide appropriate treatment and management for affected horses.
Symptoms of Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses and can cause abnormal movement in their hind limbs. It is characterized by sudden and exaggerated flexion of one or both hind legs. This condition can be quite alarming for horse owners, and it is important to recognize the symptoms of stringhalt to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Here are the common symptoms of stringhalt in horses:
- Uncontrolled upward movement of the hind legs: One of the most noticeable symptoms of stringhalt is the involuntary and exaggerated flexion of the hind legs. When a horse with stringhalt walks or trots, their hind legs may suddenly jerk upward towards their belly or chest. This movement can be sporadic or continuous, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Stiffness and lameness: Horses with stringhalt may exhibit stiffness and lameness in their hind limbs. They may have difficulty walking, trotting, or turning, and their movements may appear abnormal or uncoordinated. The stiffness and lameness can vary in intensity, depending on the individual horse and the stage of the condition.
- Difficulty backing up: Horses with stringhalt often find it challenging to back up. They may have trouble coordinating the movement of their hind limbs, making it difficult for them to reverse or maneuver in tight spaces.
- Hesitation or reluctance to move: Some horses with stringhalt may show hesitation or reluctance to move. They may appear hesitant to take steps or may resist moving altogether. This can be due to the discomfort or imbalance caused by the abnormal flexion of their hind legs.
- Pain or discomfort: In severe cases of stringhalt, horses may experience pain or discomfort in their hind limbs. They may exhibit signs of distress, such as flinching, tail swishing, or vocalization. It is important to monitor the horse closely for any signs of pain or discomfort and seek veterinary attention if necessary.
It is crucial to note that the severity of stringhalt symptoms can vary between individual horses. Some horses may display mild symptoms that are barely noticeable, while others may have more pronounced and debilitating symptoms. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing stringhalt and ensuring the well-being of the affected horse.
Diagnosing Stringhalt in Horses
In this section, we will discuss the process of diagnosing stringhalt in horses. Stringhalt is a condition that affects the movement of a horse’s hind limbs, causing them to exhibit involuntary jerking or exaggerated flexion. It can be a debilitating condition that affects a horse’s ability to move and perform daily activities.
When a horse shows signs of stringhalt, it is important to diagnose the condition promptly to determine the appropriate treatment and management strategies. The diagnostic process involves a thorough examination and assessment of the horse’s symptoms and overall health.
1. History and Observation
The first step in diagnosing stringhalt is to obtain a detailed history of the horse’s symptoms and any recent changes in behavior or environment. This includes information about the onset and progression of the stringhalt symptoms, as well as any relevant medical history or prior injuries.
Observation of the horse’s gait and movement is also crucial. The veterinarian will carefully watch the horse as it walks, trots, and moves in various directions to assess the extent and frequency of the stringhalt episodes. They will also observe the horse at rest to identify any other potential signs of muscle or neurological abnormalities.
2. Physical Examination
The next step involves a comprehensive physical examination of the horse. The veterinarian will assess the horse’s overall body condition, muscle tone, and any signs of lameness or pain. They will palpate the horse’s limbs, joints, and muscles to check for any abnormalities or areas of discomfort.
During the physical examination, the veterinarian may also perform specialized tests to further evaluate the horse’s muscle function and nerve responses. This may include flexion tests, where specific joints are flexed and held for a period of time to assess the horse’s reaction and any associated pain or stiffness.
3. Diagnostic Imaging
In some cases, diagnostic imaging techniques may be necessary to obtain more detailed information about the horse’s condition. This can help identify any structural abnormalities or underlying causes of the stringhalt symptoms.
X-rays may be taken to evaluate the horse’s bones and joints for any fractures, arthritis, or other abnormalities. Ultrasound imaging can be used to assess the soft tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, for any signs of damage or inflammation.
4. Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are often performed to rule out other potential causes of the horse’s symptoms and to assess overall health. Blood tests can help identify any underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, or metabolic imbalances that may contribute to the development of stringhalt.
In some cases, a muscle biopsy may be recommended to evaluate the horse’s muscle tissue for any abnormalities or signs of disease.
5. Neurological Evaluation
Given that stringhalt can be associated with neurological conditions, a thorough neurological evaluation is essential. The veterinarian will assess the horse’s reflexes, coordination, and responses to sensory stimuli. This helps determine if there are any underlying neurological issues contributing to the stringhalt symptoms.
Summary
Diagnosing stringhalt in horses involves a comprehensive approach, including obtaining a detailed history, observing the horse’s gait and movement, performing a physical examination, utilizing diagnostic imaging techniques, conducting laboratory tests, and evaluating the horse’s neurological function. It is crucial to identify the underlying cause of stringhalt to develop an effective treatment plan and improve the horse’s quality of life.
Treatment Options for Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses and is characterized by involuntary, exaggerated movements of the hind legs. The exact cause of stringhalt is still unknown, but it is believed to be associated with nerve damage or a neurological disorder. The condition can significantly affect a horse’s gait and overall performance, making it essential to explore treatment options.1. Surgical Intervention
In severe cases of stringhalt, surgical intervention may be considered. One surgical procedure called tenotomy involves cutting the tendon responsible for the exaggerated movement, known as the lateral digital extensor tendon. This procedure aims to alleviate the symptoms and improve the horse’s gait. However, it is important to note that surgery is not always a viable option and should be thoroughly discussed with a veterinarian.2. Medication
Medications can be used to manage the symptoms of stringhalt and provide relief to the affected horse. One commonly prescribed medication is phenytoin, an anticonvulsant drug that helps reduce muscle hyperactivity. It works by affecting the central nervous system, reducing the exaggerated movements associated with stringhalt. Other medications, such as muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatories, may also be prescribed depending on the individual horse’s condition and response to treatment.3. Alternative Therapies
In addition to traditional medical treatments, some horse owners may opt for alternative therapies to help manage stringhalt symptoms. These therapies include acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy. While the effectiveness of these treatments may vary, they can provide additional support and potentially improve the horse’s overall well-being. It is crucial to consult with a qualified professional experienced in equine alternative therapies before pursuing these options.4. Dietary Changes
Diet can play a role in managing stringhalt symptoms. Some horse owners have reported improvements in their horse’s condition by adjusting their diet. A diet rich in Vitamin E and Omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation and support nerve health. It is advisable to consult with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to formulate a diet plan tailored to the horse’s specific needs.5. Exercise and Rehabilitation
Regular exercise and rehabilitation can aid in managing stringhalt symptoms. Controlled exercise routines, such as lunging or ground work, can help improve muscle strength and coordination. Additionally, physical therapy exercises, such as stretching and massage, may help alleviate muscle tension and improve overall mobility. It is essential to work closely with a veterinarian or qualified equine rehabilitation specialist to develop an appropriate exercise and rehabilitation plan for each horse.6. Management Changes
Stringhalt can be managed by making certain changes in the horse’s management practices. Providing ample turnout time in a safe and spacious environment can help reduce stress and provide necessary exercise. Ensuring proper hoof care and regular farrier visits can also contribute to maintaining proper balance and gait. Additionally, avoiding rough terrain or excessively hard surfaces can prevent further strain on the horse’s legs. In summary, stringhalt in horses can be a challenging condition to manage effectively. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the symptoms and the individual horse’s response to therapy. Surgical intervention, medication, alternative therapies, dietary changes, exercise, and rehabilitation, as well as management adjustments, are all potential avenues to explore. However, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian experienced in equine health to determine the best course of action for each affected horse.Preventing Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses, causing involuntary and exaggerated movements of the hind legs. This condition can be distressing for both the horse and the owner, as it can cause discomfort and affect the horse’s ability to move properly. While the exact cause of stringhalt is still unknown, there are certain measures that can be taken to help prevent this condition in horses.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
One of the key factors in preventing stringhalt in horses is maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet. Horses should have access to high-quality forage and be fed a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs. It is important to provide horses with a diet that is appropriate for their age, size, and activity level. A diet that is deficient in certain essential nutrients can increase the risk of developing stringhalt.
Ensure Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a horse’s overall health and preventing various conditions, including stringhalt. Exercise helps to keep the horse’s muscles strong and flexible, reducing the risk of developing muscle imbalances that can contribute to stringhalt. It is important to provide horses with regular turnout and exercise opportunities, allowing them to move freely and engage in natural behaviors.
Proper Hoof Care
Good hoof care is crucial in maintaining a horse’s overall well-being and preventing conditions like stringhalt. Regular trimming and shoeing by a qualified farrier help to ensure proper hoof balance and support. Uneven or imbalanced hooves can put strain on the horse’s musculoskeletal system, potentially leading to gait abnormalities and an increased risk of developing stringhalt.
Minimize Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can have a negative impact on a horse’s health and increase the risk of developing various conditions, including stringhalt. It is important to provide horses with a safe and secure environment that minimizes stressors. This includes providing adequate turnout time, social interaction with other horses, and reducing exposure to loud noises or sudden changes in routine.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential in maintaining a horse’s overall health and detecting any potential issues early on. A veterinarian can assess a horse’s well-being, identify any underlying health conditions, and provide appropriate treatment if necessary. Early intervention can help prevent the progression of conditions like stringhalt and minimize the impact on the horse’s quality of life.
In summary, while the exact cause of stringhalt in horses is still unknown, there are measures that can be taken to help prevent this condition. Maintaining a balanced diet, providing regular exercise, ensuring proper hoof care, minimizing stress and anxiety, and scheduling regular veterinary check-ups are all important in reducing the risk of stringhalt in horses. By implementing these preventative measures, horse owners can help keep their equine companions healthy and sound.

FAQs
What is stringhalt in horses?
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses’ movement, causing their hind legs to jerk or rapidly lift higher than normal. It can be caused by various factors such as nerve damage, toxicity, or nutritional deficiencies. Stringhalt can result in difficulty walking, stumbling, and an abnormal gait.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stringhalt in horses is a neurological disorder that affects the hind limbs, causing abnormal and exaggerated movements. It is important for horse owners and caretakers to become familiar with the signs and symptoms of stringhalt, such as the sudden lifting and bending of the hind legs. Prompt veterinary attention is crucial for diagnosing and managing this condition. Treatment options may include medication, surgical intervention, and physical therapy to alleviate the discomfort and improve the horse’s quality of life. Additionally, implementing preventive measures, such as regular exercise, proper nutrition, and maintaining a safe environment, can help reduce the risk of stringhalt.
Overall, being knowledgeable about stringhalt and its management can contribute to the well-being and soundness of horses, ensuring their optimal performance and enjoyment in various activities.
