Stringhalt in horses is a neurological condition that affects the hind limbs, causing involuntary and exaggerated movements. It is characterized by sudden and abnormal flexion or hyperextension of the hocks and/or hind legs. This condition can occur in one or both hind limbs and may vary in severity. While the exact cause of stringhalt is not fully understood, it is believed to be related to nerve dysfunction. Stringhalt can significantly impact a horse’s gait, leading to lameness and difficulty in performing everyday activities.
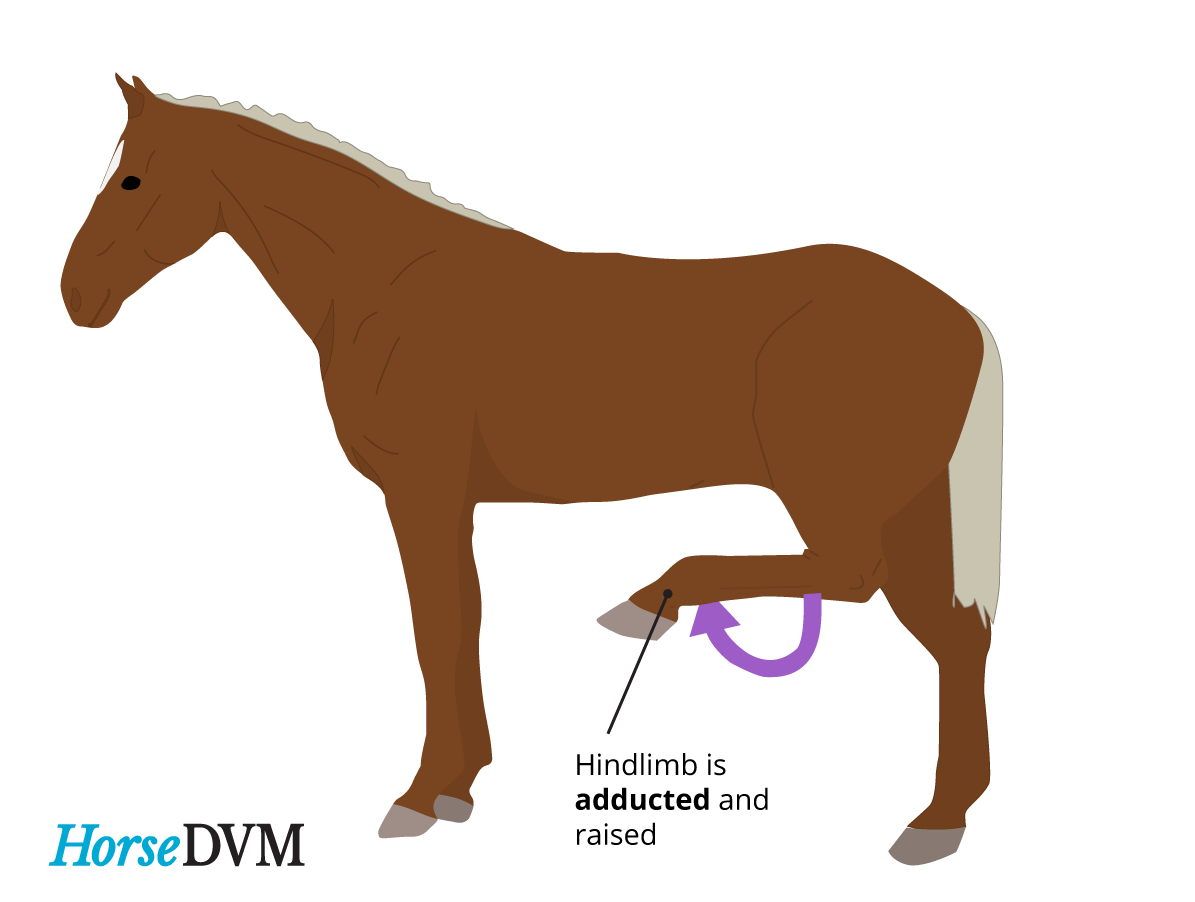
Diagnosing and Treating Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses and can cause them to exhibit abnormal movements in their hind legs. It is important for horse owners and caretakers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of stringhalt, as early detection and treatment can lead to a better prognosis for the affected horse. In this section, we will discuss the process of diagnosing stringhalt in horses and explore the various treatment options available.
Diagnosis of Stringhalt
When a horse is suspected of having stringhalt, it is crucial to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis. The veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination and evaluate the horse’s gait and movement. They may also conduct additional tests such as nerve blocks or radiographs to rule out other potential causes of the abnormal movements.
One of the telltale signs of stringhalt is the exaggerated flexion of the affected hind limb(s) when the horse is walking or trotting. The horse may exhibit a sudden and involuntary upward movement of the leg, often referred to as a “hitch.” This abnormal movement is usually more pronounced when the horse is turning or backing up.
In some cases, the veterinarian may also observe muscle atrophy or weakness in the hindquarters of the affected horse. This can further support the diagnosis of stringhalt. However, it is important to note that the symptoms of stringhalt can vary in severity from horse to horse.
Treatment Options
Once a horse is diagnosed with stringhalt, there are several treatment options available depending on the severity of the condition. The aim of treatment is to alleviate the symptoms and improve the horse’s quality of life.
1. Conservative Management: In mild cases of stringhalt, conservative management may be sufficient. This involves providing the horse with rest and reducing strenuous activities. Additionally, therapeutic shoeing or trimming may be recommended to help improve the horse’s gait and minimize the abnormal movements.
2. Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage the symptoms of stringhalt. Antispasmodic drugs, such as phenytoin or carbamazepine, can help reduce the involuntary muscle contractions and alleviate the hitching movements. However, it is important to note that these medications may not be effective in all horses and can have potential side effects.
3. Surgical Intervention: In severe cases of stringhalt or when conservative management and medication fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered. The most common surgical procedure for stringhalt is a neurectomy, which involves selectively cutting or removing the affected nerve(s) to reduce the abnormal muscle contractions. It is important to consult with a veterinarian to determine if surgery is a suitable option for the horse.
Post-Treatment Care
Regardless of the chosen treatment option, post-treatment care is essential for the recovery and well-being of the horse. This may involve physical therapy, exercise regimens, and regular follow-up visits with the veterinarian to monitor the horse’s progress. It is important to provide a suitable environment for the horse to prevent any further injuries or exacerbation of the condition.
In summary, stringhalt is a condition that can significantly affect a horse’s mobility and quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment options, including conservative management, medications, or surgical intervention, can help alleviate the symptoms and improve the horse’s overall well-being. However, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to determine the best course of action for each individual horse.

Surgical Options for Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a neuromuscular disorder that affects horses, causing abnormal and exaggerated flexion of one or both hind limbs. It can significantly impact a horse’s gait and overall mobility. While there are various treatment approaches for stringhalt, surgical options are sometimes considered when other conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief. In this section, we will explore some surgical options that can help manage stringhalt in horses.
1. Neurectomy
Neurectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of a portion of the affected horse’s lateral digital nerve. This nerve is responsible for transmitting signals to the flexor muscles in the hind limb. By removing a section of this nerve, it disrupts the abnormal signals and can help alleviate the symptoms of stringhalt.
During the neurectomy procedure, the horse is placed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision in the affected limb and carefully locates the lateral digital nerve. A segment of the nerve is then excised, and the incision is sutured closed. After the surgery, the horse may require a period of post-operative care and rehabilitation.
It is important to note that neurectomy is not a permanent solution for stringhalt, as the nerve has the potential to regenerate over time. However, in many cases, the symptoms of stringhalt are significantly reduced or even eliminated for a considerable period.
2. Tenotomy
Tenotomy is another surgical option that can be considered for horses with severe stringhalt. This procedure involves the cutting or lengthening of the affected horse’s lateral or medial digital extensor tendon. By altering the tension in the tendon, the abnormal flexion of the limb can be corrected or improved.
The tenotomy procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon carefully exposes the affected tendon and makes a precise incision or lengthens the tendon as needed. After the procedure, the limb is immobilized and a period of rest and rehabilitation follows.
Tenotomy can be an effective treatment option, especially for horses with severe cases of stringhalt. However, it is important to consider the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure, such as wound healing issues or the development of tendon adhesions.
3. Fasciotomy
Fasciotomy is a surgical procedure that involves the release or removal of the fascial attachments around the affected horse’s peroneus tertius muscle. This muscle is often implicated in cases of stringhalt. By releasing the tension on the muscle, the abnormal flexion can be improved.
During the fasciotomy procedure, the horse is placed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision near the affected muscle and carefully dissects the fascial attachments. The tension is released, and the incision is closed. Post-operative care and rehabilitation are necessary to ensure proper healing and recovery.
Fasciotomy can be a viable option for horses with stringhalt, particularly when other surgical approaches are not suitable. However, it is important to note that the procedure may not completely eliminate the symptoms and that the horse may still have some residual abnormal flexion.
In summary, surgical options can be considered for horses with stringhalt when conservative treatments fail to provide sufficient improvement. Neurectomy, tenotomy, and fasciotomy are some of the surgical approaches that can be used to manage the symptoms of stringhalt. It is important to work closely with a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate surgical option based on the individual horse’s condition and overall health. As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications that should be carefully considered before making a decision.
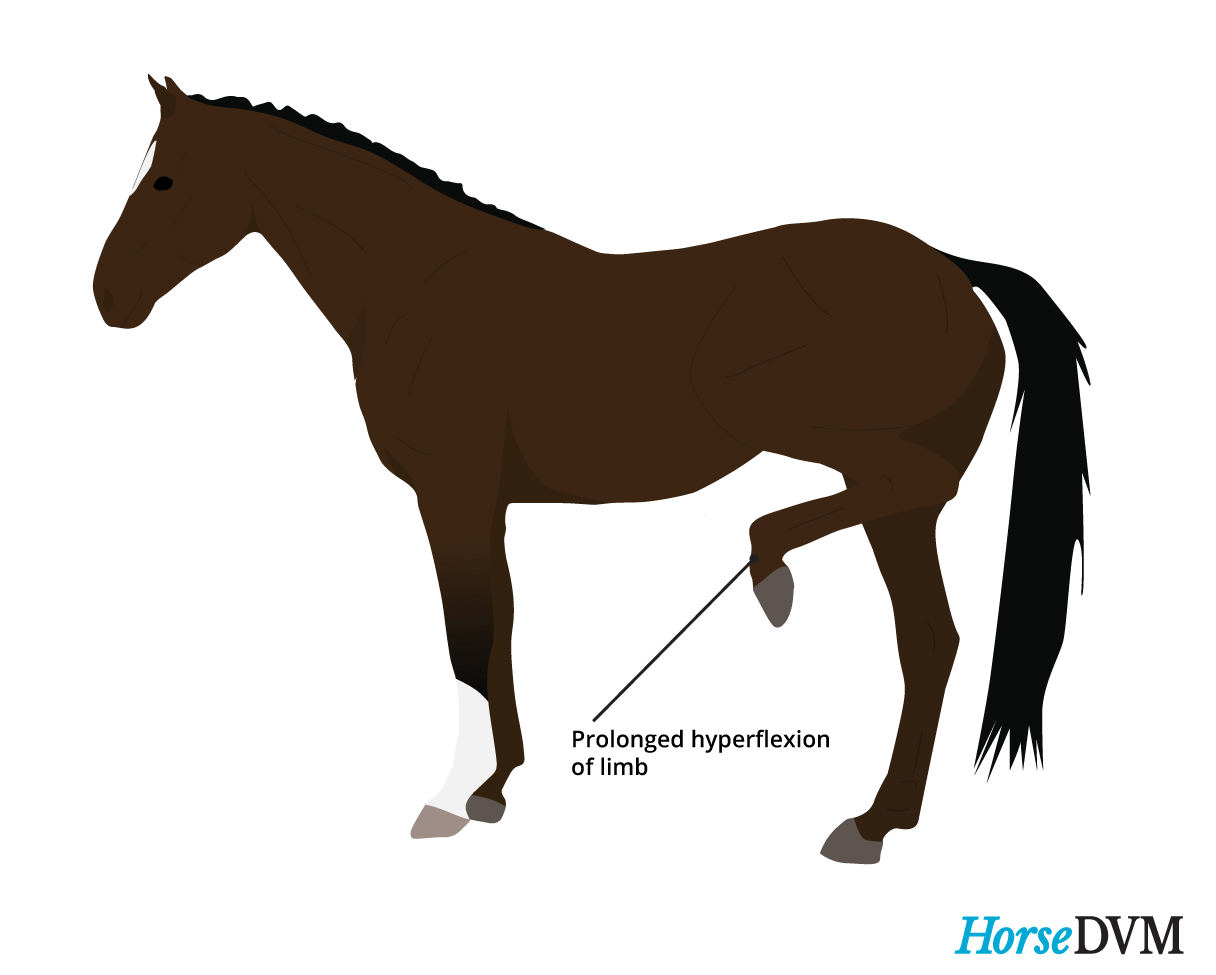
Preventing and Managing Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses, causing involuntary and exaggerated movements of the hind limbs. It is characterized by sudden and jerky movements, where the affected leg is pulled up excessively towards the belly. This condition can be quite uncomfortable and can interfere with a horse’s normal movement and performance. In this section, we will discuss some preventive measures and management strategies for stringhalt in horses.
1. Diet and Nutrition
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of horses. When it comes to preventing stringhalt, it is important to ensure that horses receive adequate nutrition. This includes providing a diet rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins. Consult with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to determine the specific dietary needs of your horse and make any necessary adjustments.
2. Exercise and Conditioning
Regular exercise and conditioning are vital for maintaining the strength and flexibility of a horse’s muscles and joints. It is recommended to incorporate a variety of exercise activities into the horse’s routine, including stretching exercises, lunging, and riding. Building up the horse’s fitness gradually can help prevent injuries and reduce the risk of developing stringhalt.
3. Proper Farrier Care
A professional farrier can play a significant role in the prevention and management of stringhalt. Regular trimming and balancing of hooves are important for maintaining proper weight distribution and minimizing the risk of lameness. A skilled farrier can also detect any abnormalities or imbalances in the horse’s gait and make appropriate corrective measures.
4. Environmental Management
The environment in which a horse lives and spends a significant amount of time can impact their overall health and well-being. It is important to ensure that the horse’s living area is clean, well-maintained, and free from potential hazards. Regularly inspect paddocks and stables for any uneven surfaces, obstacles, or dangerous objects that may contribute to accidents or injuries.
5. Minimize Stress and Anxiety
Horses are sensitive animals and are prone to stress and anxiety, which can exacerbate certain conditions, including stringhalt. Minimizing stressors in the horse’s environment can help reduce the risk of developing or worsening symptoms. Providing a calm and secure living environment, incorporating regular turnout, and implementing positive reinforcement training techniques can all contribute to minimizing stress levels in horses.
6. Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary check-ups and ongoing care are essential for the early detection and management of stringhalt. A veterinarian can conduct a thorough examination and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the severity of the condition. They may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, or in severe cases, surgical intervention.
7. Monitoring and Observation
Closely monitoring and observing your horse’s behavior and movement patterns can help in detecting any early signs of stringhalt. Pay attention to changes in gait, stiffness, or any abnormal movements. Promptly reporting any concerns to your veterinarian can aid in early intervention and prevent further progression of the condition.
In summary, preventing and managing stringhalt in horses involves a combination of proper diet and nutrition, regular exercise, appropriate farrier care, maintaining a safe environment, minimizing stress, seeking veterinary care, and closely monitoring the horse’s behavior. By following these preventive measures and implementing effective management strategies, horse owners can help ensure the well-being and optimal performance of their equine companions.
Understanding the Long-term Effects of Stringhalt on Horses
Stringhalt is a neurological disorder that affects horses, causing involuntary and exaggerated lifting of one or both hind legs. This condition can have long-term effects on a horse’s overall health and functionality. In this section, we will delve deeper into understanding the long-term effects of stringhalt on horses.
1. Decreased Mobility and Performance: Horses with stringhalt often experience a significant decrease in their mobility and overall performance. The exaggerated leg movements make it challenging for the horse to move smoothly and efficiently, which can affect their ability to participate in various activities such as riding, jumping, or even basic daily tasks.
2. Pain and Discomfort: Stringhalt can cause pain and discomfort in affected horses. The abnormal leg movements can put strain on the horse’s muscles, tendons, and joints, leading to inflammation and soreness. This can significantly impact the horse’s quality of life and overall well-being.
3. Difficulty with Lameness Diagnosis: Stringhalt can often be misdiagnosed as lameness or other musculoskeletal issues. This can lead to delays in appropriate treatment and management plans for the affected horse. Understanding the long-term effects of stringhalt can help horse owners and veterinarians accurately diagnose and treat the condition.
4. Progressive Worsening: In some cases, stringhalt can progress and worsen over time. The severity of the leg movements may increase, making it even more challenging for the horse to move comfortably. This progression can further limit the horse’s mobility and performance, requiring more specialized care and management.
5. Impact on Hoof Health: The abnormal leg movements associated with stringhalt can also impact the horse’s hoof health. The uneven weight distribution and abnormal gait can lead to imbalances and uneven wear on the hooves. This can increase the risk of hoof-related issues, such as laminitis or hoof cracks.
In summary, stringhalt can have significant long-term effects on horses, including decreased mobility and performance, pain and discomfort, difficulty with lameness diagnosis, progressive worsening, and an impact on hoof health. It is essential for horse owners and veterinarians to understand these effects to provide appropriate care and management for horses affected by stringhalt.
FAQs
Q: What is a stringhalt in horses?
Stringhalt is a condition in horses that causes exaggerated and involuntary movement in the hind legs. It can result in sudden and abnormal flexion of the hock and/or upward movement of the leg. It is thought to be caused by a neurological dysfunction.
Q: What are the symptoms of stringhalt in horses?
The main symptom of stringhalt in horses is the abnormal movement of the hind legs, often seen as exaggerated flexion or jerking. Other signs may include difficulty in backing up, stumbling, and an irregular gait.
Q: How is stringhalt in horses treated?
Treatment options for stringhalt in horses may include surgery, medication, or the use of specialized shoeing techniques. However, the success of treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment plan for the affected horse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding stringhalt in horses is crucial for horse owners and caregivers. Stringhalt is a neuromuscular disorder that causes involuntary and exaggerated flexion of the hind limbs. It can be a result of various factors, such as nerve damage, toxicity, or nutritional deficiencies. Identifying the symptoms of stringhalt, such as exaggerated gait or sudden lifting of the hind legs, is essential for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. While the exact cause of stringhalt is still unknown, research and veterinary advancements have provided various management options to improve the condition and alleviate the symptoms. By staying informed and working closely with a veterinarian, horse owners can effectively care for and support horses with stringhalt.
