Knowing the appropriate places to give a horse a shot is essential for their well-being and proper medical care. Administering injections correctly ensures minimal discomfort and maximizes the effectiveness of the medication. The most common sites for injections in horses include the neck, shoulder, and hindquarters. Each area has specific advantages and considerations, such as muscle mass and proximity to major blood vessels. It is crucial to work with a veterinarian who can guide you on the precise locations and techniques for administering shots to your horse, ensuring their health and safety.

Common locations for horse injections: Finding the right spot
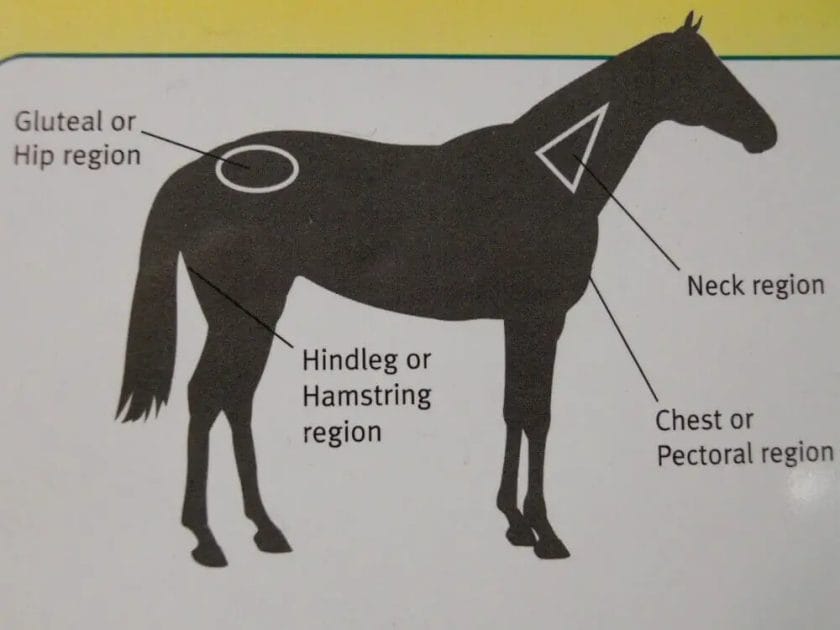
Administering injections to horses is a common practice in veterinary medicine. Whether it’s for vaccinations, medications, or supplements, knowing the proper locations for horse injections is crucial for their health and well-being. In this section, we will explore the common areas where horse injections are typically given.
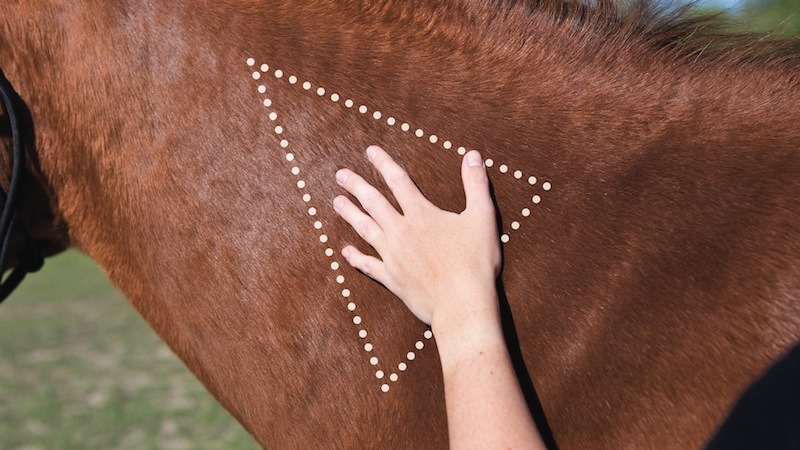
1. Neck
The neck is one of the most common locations for horse injections. It provides a large muscle mass that can handle the volume of the injection and disperses the medication effectively. When giving injections in the neck, it is important to choose the correct spot to avoid injuring vital structures.
The most common injection site in the neck is the muscles on either side of the neck, known as the neck triangle. It is located between the cervical vertebrae and the jugular vein. This area is easily accessible and provides a safe and effective location for injections.
2. Gluteal Muscles
The gluteal muscles, located in the hindquarters of the horse, are another common site for injections. This area offers a large muscle mass and allows for easy access. However, it is important to be cautious when administering injections in this area to avoid hitting the sciatic nerve.
When giving injections in the gluteal muscles, it is recommended to use the upper outer quadrant of the muscle. This area provides a safe distance from the sciatic nerve and ensures that the medication is properly absorbed.
3. Pectoral Muscles
The pectoral muscles, located in the chest area of the horse, can also be used for injections. This area is most commonly used for intramuscular injections. However, it is important to exercise caution when injecting in this area to avoid hitting vital structures such as the lungs or major blood vessels.
When administering injections in the pectoral muscles, it is advisable to target the middle of the muscle to minimize the risk of injury. It is also important to note that this area may not be suitable for all types of injections, so consulting with a veterinarian is recommended.
4. Inner Thigh
The inner thigh is another location where horse injections can be given. This area provides a good amount of muscle mass and is easily accessible. However, it is important to be cautious when injecting in this area to avoid hitting the femoral artery.
When administering injections in the inner thigh, it is advisable to target the upper third of the muscle. This area allows for proper absorption of the medication while minimizing the risk of injury.
5. Chest or Sternum
The chest or sternum area can be used for certain types of injections, such as intravenous injections or jugular catheter placements. This area provides easy access to the jugular vein and can be convenient for procedures that require direct access to the bloodstream.
When using the chest or sternum area for injections, it is important to follow proper sterile techniques to prevent infections. It is also essential to consult with a veterinarian to ensure safe and accurate administration of the injection.
Summary
Administering injections to horses requires careful consideration of the injection site. The neck, gluteal muscles, pectoral muscles, inner thigh, and chest or sternum are common locations used for horse injections. Each site has its own advantages and considerations, and it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate location for specific injections.
By following proper techniques and guidelines, horse owners and caretakers can ensure the safe and effective administration of injections, promoting the health and well-being of their equine companions.
Tips for administering shots to horses: Ensuring proper dosage
Administering shots to horses is a crucial part of their healthcare routine. Whether it’s for vaccinations, medications, or supplements, it’s important to ensure that the correct dosage is given to the horse. Here are some tips to help you administer shots to horses and ensure proper dosage:
1. Consult a veterinarian:
Before administering any shots to your horse, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian. They can provide guidance on the specific vaccinations or medications your horse needs and the correct dosage for their age, weight, and health condition. Remember that every horse is unique, so it’s important to follow the veterinarian’s instructions accurately.
2. Prepare the equipment:
Prior to administering the shot, gather all the necessary equipment. This may include a syringe, needle, gloves, alcohol wipes, and the medication or vaccine. Ensure that the equipment is clean, sterile, and in good condition to avoid any contamination or infection.
3. Handling the horse:
Approach the horse calmly and confidently, as they can sense your apprehension. Use a halter or lead rope to safely restrain the horse during the process. It’s important to have a helper to hold the horse and keep them steady if needed.
4. Choose the injection site:
Select the appropriate injection site based on the medication or vaccine being administered. Common injection sites for horses include the neck, shoulder, or hip. Ensure the chosen area is clean and free from any wounds or abrasions. Avoid injecting near major blood vessels or nerves.
5. Proper needle insertion:
Hold the syringe and needle at a 45-degree angle and insert it quickly and smoothly into the chosen injection site. Avoid any sudden movements that may startle the horse. Once inserted, gently aspirate to check for blood in the syringe. If blood is present, withdraw the needle and choose a different site.
6. Administering the medication:
Slowly and steadily push the plunger to administer the medication or vaccine. Ensure that the full dosage is delivered. Avoid administering the injection too quickly, as it may cause discomfort or pain to the horse.
7. Proper disposal:
After administering the shot, safely dispose of the used needle and syringe in a puncture-proof container. Follow the proper disposal guidelines to prevent any accidental injuries or contamination.
8. Monitor the horse:
Keep a close eye on the horse after administering the shot. Watch for any signs of adverse reactions, such as swelling, redness, or lameness. If you notice any unusual symptoms, contact your veterinarian immediately.
9. Maintain proper records:
Keep detailed records of the shots administered to your horse, including the date, dosage, and any associated reactions. This information will be valuable for future reference and to ensure the horse’s healthcare regimen is up to date.
In summary, administering shots to horses requires careful attention and proper dosage. Consulting a veterinarian, preparing the equipment, handling the horse safely, choosing the correct injection site, and administering the medication correctly are all essential steps. Proper disposal of used needles and syringes, monitoring the horse for any adverse reactions, and maintaining accurate records are also important aspects of administering shots to horses.

How to Give a Horse an Intramuscular Injection: Step-by-Step Instructions
Administering medications to horses is a crucial part of their healthcare routine. While some medications can be given orally or topically, certain drugs are best administered through intramuscular injections. If you’re a horse owner or caretaker, it’s important to know how to safely and effectively give your horse an intramuscular injection. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure a smooth and successful injection process:
Step 1: Gather Your Supplies
Before administering any injection, it is essential to gather all the necessary supplies. Here’s what you’ll need:
- A sterile syringe appropriate for the dose
- A new, sterile needle of the correct size
- The medication prescribed by your veterinarian
- Alcohol swabs or another disinfectant
- Gloves
- A clean, well-lit area to work in
Step 2: Prepare the Medication
Once you’ve gathered all the supplies, carefully read the medication label and follow the instructions for preparation. Some medications may require mixing or diluting before use. Ensure that you have the correct dosage and that the medication is ready for administration.
Step 3: Choose the Injection Site
Selecting the appropriate injection site is crucial for the safety and comfort of your horse. The most common injection sites for intramuscular injections in horses are the neck and rump muscles. These areas provide sufficient muscle mass and are relatively easy to access.
Step 4: Prepare the Injection Site
Before administering the injection, it’s important to prepare the injection site properly. Start by cleaning the area with an alcohol swab or disinfectant to minimize the risk of infection. Allow the area to dry before proceeding.
Step 5: Restrain the Horse
To ensure your safety and that of the horse, it’s crucial to have someone hold or restrain the horse during the injection process. This will prevent any sudden movements or reactions that could result in injury.
Step 6: Assemble the Syringe
Attach the sterile needle to the syringe securely. Make sure it is tightly fastened to prevent any leakage or detachment during the injection.
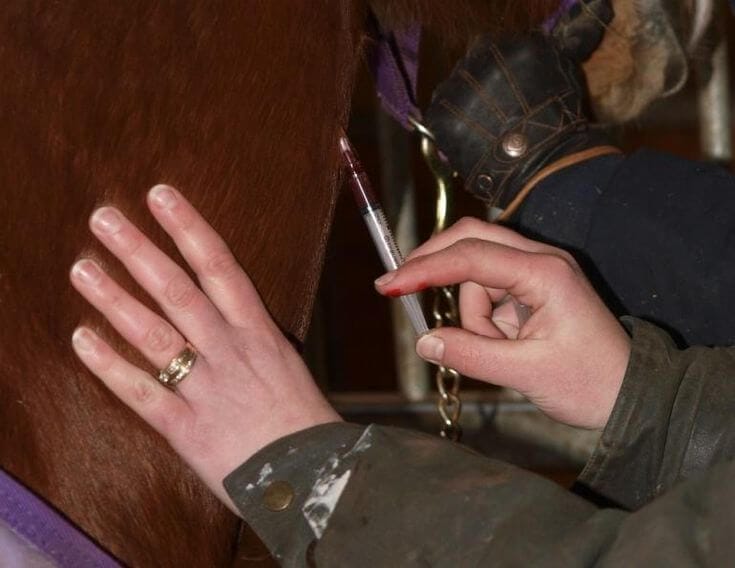
Step 7: Insert the Needle
With the needle attached to the syringe, insert it swiftly and smoothly into the chosen injection site. Aim for the center of the muscle and penetrate at a 90-degree angle to ensure proper placement.
Step 8: Aspirate and Inject
Once the needle is inserted, gently pull back on the plunger of the syringe. If blood appears in the syringe, you may have accidentally hit a blood vessel, and you should withdraw and select a new injection site. If no blood is present, slowly depress the plunger to administer the medication into the muscle.
Step 9: Withdraw the Needle
After the medication has been fully administered, carefully withdraw the needle from the injection site. Apply pressure to the site with a clean cotton ball or gauze pad to minimize any bleeding.
Step 10: Proper Waste Disposal
Dispose of the used needle and syringe safely and appropriately. Sharps containers are designed specifically for this purpose and can be obtained from your veterinarian or local pharmacy.
In summary, giving a horse an intramuscular injection requires careful preparation, proper technique, and a calm and controlled environment. By following these step-by-step instructions, you can ensure the health and well-being of your horse through safe and effective medication administration.
Safest Areas to Give a Horse a Shot: Minimizing Discomfort and Maximizing Effectiveness
Administering medication to horses is a routine part of their healthcare. Whether it’s vaccinations, antibiotics, or other types of injections, it’s important to know the safest areas to give a horse a shot. By choosing the right injection site, you can minimize discomfort for the horse while ensuring the effectiveness of the medication. In this section, we will explore the various areas on a horse’s body that are commonly used for injections and discuss the factors to consider when selecting an injection site.
1. Neck muscles
The neck is one of the most common areas used for giving injections to horses. The neck muscles provide a large and well-defined injection site, making it easier to administer the medication accurately. When giving a shot in the neck, it is recommended to aim for the muscular area located halfway down the neck. This area is generally safe and minimizes the risk of hitting any major blood vessels or nerves.
However, it is essential to avoid injecting near the jugular vein, which runs along the side of the horse’s neck. Injecting into or too close to this vein can lead to potential complications and discomfort for the horse. Proper technique and precision are required to ensure a safe and effective injection in the neck muscles.
2. Pectoral muscles
The pectoral muscles, located on the horse’s chest, can also serve as a suitable injection site. These muscles are well-developed and provide a stable area for administering injections. When using the pectoral muscles, it’s important to select an area that is free from blemishes, wounds, or sensitive areas.
Injections in the pectoral muscles may be particularly useful for horses that are sensitive or reactive to injections in other areas. However, it is crucial to be cautious when giving shots in this region to avoid accidentally hitting bone or other vital structures beneath the muscles.
3. Gluteal muscles
The gluteal muscles, located in the hindquarters of the horse, can be another option for giving injections. These muscles are relatively large and provide a suitable injection site for medications that require deeper penetration, such as intramuscular injections.
When administering shots in the gluteal muscles, it’s essential to avoid the sciatic nerve and the bony prominences known as the tuber coxae. Injecting near these sensitive areas can cause discomfort or injury to the horse. Careful consideration of the injection technique and proper anatomical knowledge is crucial when utilizing the gluteal muscles as an injection site.
4. Inner thigh muscles
The inner thigh muscles, located on the inside of the horse’s hind leg, can be utilized for certain types of injections. This area offers a relatively accessible and convenient site for administering medications.
When selecting the inner thigh muscles as an injection site, it’s important to ensure that the horse is comfortable and tolerant of the procedure. Some horses may be more sensitive in this area, and extra care should be taken to minimize any potential discomfort or adverse reactions.
5. Consult with a veterinarian
While the areas mentioned above are commonly used for giving injections to horses, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian before administering any medication. A veterinarian can provide specific guidance based on the type of medication, the horse’s individual needs, and any specific health considerations.
In summary, when giving a horse a shot, it is important to choose the safest areas to minimize discomfort and maximize effectiveness. The neck muscles, pectoral muscles, gluteal muscles, and inner thigh muscles are commonly used injection sites. However, it is essential to exercise caution and precision to avoid hitting major blood vessels, nerves, bones, or sensitive areas. Consulting with a veterinarian is always recommended to ensure the proper administration of medication and the well-being of the horse.
FAQs
1. Where should I give a horse a shot?
You should give a horse a shot in the muscle, generally in the neck or rump area. These locations have thicker muscle tissue which helps in better absorption of the medication. It is important to consult a veterinarian for proper guidance on administering injections and to ensure the safety and well-being of the horse.
2. What is the recommended vaccination schedule for horses?
The recommended vaccination schedule for horses may vary depending on factors such as location, age, and specific health considerations. Generally, horses should receive core vaccinations for diseases such as tetanus, rabies, and Eastern and Western equine encephalomyelitis. It is best to consult a veterinarian who can provide a tailored vaccination plan for your horse.
3. How often should I deworm my horse?
Horses should be dewormed regularly to prevent internal parasite infestations. The frequency of deworming depends on factors such as age, environment, and individual horse risk. It is generally recommended to deworm horses every 6-8 weeks, but again, consulting a veterinarian is crucial to develop a deworming program suitable for your horse’s specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, administering a shot to a horse requires skill and caution to ensure the animal’s well-being. It is vital to locate the appropriate injection site, such as the neck or hip muscle, to minimize discomfort and avoid injury. A veterinarian or trained professional should be consulted to determine the precise location and technique for administering a shot to a horse. Remember to use sterile equipment and follow proper hygiene practices during the entire process. Safely giving a horse a shot is crucial for their health and requires careful attention to detail.
To conclude, always prioritize the horse’s safety and welfare when giving a shot. Being knowledgeable about the correct injection site and technique is essential to prevent any harm or complications. Veterinary guidance is highly recommended to ensure accurate administration and dosage. It is vital to use sterile equipment, maintain a hygienic environment, and follow proper disposal procedures for needles and other medical waste. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the horse receives the necessary medication or treatment in a safe and effective manner.

