Cellulitis in horses is a common and potentially serious condition that affects the soft tissues of the legs and other areas. It is characterized by inflammation and swelling, which can be accompanied by pain, heat, and lameness. Cellulitis can be caused by a bacterial infection that enters the body through a wound or skin puncture. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and promote a speedy recovery. Understanding the symptoms and risk factors of cellulitis can help horse owners take proactive measures to prevent, manage, and treat this condition effectively.
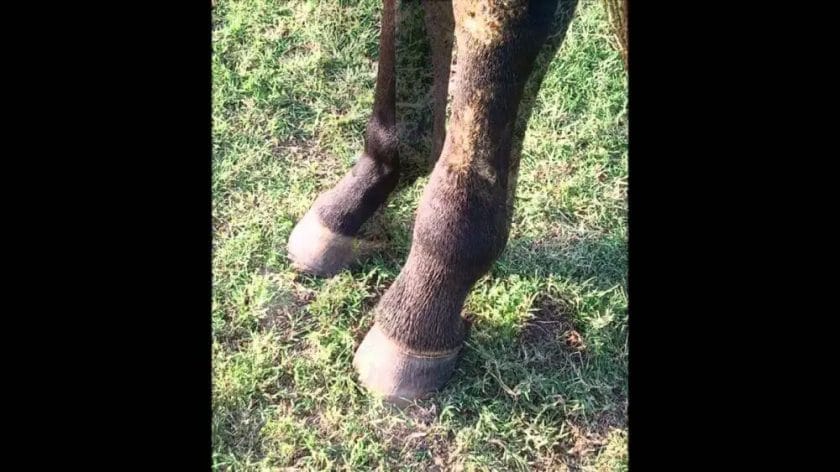
Symptoms and Signs of Cellulitis in Horses
Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection that affects the skin and underlying tissues of horses. It can occur when bacteria enter through a break in the skin, such as a wound or puncture. Recognizing the symptoms and signs of cellulitis is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
1. Swelling and Heat
One of the primary signs of cellulitis in horses is swelling and heat in the affected area. The skin may appear puffy and filled with fluid, and it may feel warmer than the surrounding healthy tissue. The swelling can vary in severity, ranging from mild to severe.
2. Pain and Discomfort
Horses with cellulitis often experience pain and discomfort in the affected area. They may show signs of lameness, reluctance to bear weight on the affected limb, and exhibit signs of distress or agitation. It is important to observe the horse’s behavior and look for any signs of pain during movement.
3. Redness and Inflammation
The infected area may appear red and inflamed, with the color extending beyond the immediate site of the wound. The inflammation may be accompanied by tenderness and sensitivity to touch. It is important to note that cellulitis can spread rapidly, so keeping an eye on any changes in color and inflammation is essential.
4. Discharge or Pus
In some cases, cellulitis may lead to the formation of discharge or pus at the site of infection. This may appear as a thick, yellowish fluid oozing from the wound. The presence of discharge indicates an ongoing infection and may require veterinary attention.
5. Fever and Systemic Signs
In more severe cases, horses with cellulitis may develop a fever. The horse’s body temperature may be elevated, and they may exhibit other systemic signs such as lethargy, loss of appetite, and elevated heart rate. These signs indicate a more serious infection and should be addressed promptly.
6. Rapid Progression
Cellulitis can progress rapidly, especially if left untreated. It is important to monitor the infected area closely for any changes. If the swelling, redness, or other symptoms worsen or spread to other areas, it is crucial to seek veterinary assistance immediately.
Remember, early detection and proper treatment are vital in managing cellulitis in horses. If you suspect your horse may have cellulitis, it is recommended to consult a veterinarian for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment plan.

Treatment Options for Cellulitis in Horses
In this section, we will discuss the various treatment options available for cellulitis in horses. Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection that affects the skin and underlying tissues of horses. The condition can cause pain, inflammation, and swelling, and if left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications. Therefore, prompt and effective treatment is essential to manage cellulitis in horses and prevent further complications.
1. Antibiotics
One of the primary treatment options for cellulitis in horses is the administration of antibiotics. Antibiotics are used to eliminate the bacterial infection and reduce inflammation. The specific type of antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the horse’s overall health. It is crucial to follow the veterinarian’s instructions regarding the dosage and duration of antibiotic treatment.
2. Bandaging
Bandaging is an important part of the treatment plan for cellulitis in horses. It helps reduce swelling, provide support to the affected limb, and prevent further contamination. The bandage should be applied correctly to ensure proper compression without compromising blood circulation. Regular monitoring and changing of the bandage are necessary to prevent complications such as pressure sores or swelling.
3. Warm Compresses
Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with cellulitis. The warmth helps increase blood flow, which aids in the healing process. It is essential to use a clean compress and avoid excessive heat to prevent burns or further damage to the skin. Warm compresses can be used in conjunction with other treatment options to enhance their effectiveness.
4. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as phenylbutazone or flunixin meglumine, may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation in horses with cellulitis. These medications can help improve the horse’s comfort and facilitate recovery. However, it is crucial to use NSAIDs under veterinary guidance and follow the recommended dosage to avoid adverse effects.
5. Supportive Care
In addition to specific treatments, providing supportive care is essential for horses with cellulitis. This includes ensuring a clean and comfortable environment, proper nutrition, and hydration. Regular exercise, as recommended by the veterinarian, can also help improve blood circulation and aid in the healing process. Monitoring the horse’s progress closely and seeking veterinary advice for any changes or concerns is crucial for successful treatment.
6. Surgical Intervention
In severe cases of cellulitis, surgical intervention may be necessary. This is typically reserved for situations where there is an abscess or fluid accumulation that needs to be drained. Surgical treatment aims to remove the infected material and promote healing. The decision for surgery will depend on the veterinarian’s assessment of the horse’s condition and the potential benefits of the procedure.
7. Follow-Up Care
After the initial treatment, follow-up care is essential to monitor the horse’s progress and prevent relapse. The veterinarian may recommend regular check-ups, wound care, or additional treatments as necessary. It is crucial to communicate any concerns or changes in the horse’s condition to the veterinarian to ensure appropriate care and prevent complications.
In summary, the treatment options for cellulitis in horses include antibiotics, bandaging, warm compresses, NSAIDs, supportive care, surgical intervention, and follow-up care. Prompt and appropriate treatment, along with proper wound management, is essential to manage cellulitis effectively and prevent complications. It is crucial to work closely with a veterinarian to develop a tailored treatment plan based on the horse’s individual needs and to ensure a successful outcome.

Prevention and Management of Cellulitis in Horses
Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection that affects the soft tissues of horses. It can cause considerable pain, discomfort, and swelling in the affected area. Proper prevention and management strategies are crucial to minimize the risk and severity of cellulitis in horses. In this section, we will discuss some effective measures to prevent and manage cellulitis in horses.
1. Maintaining good hygiene
One of the key preventive measures against cellulitis in horses is maintaining good hygiene practices. Regularly cleaning and grooming your horse can help keep their skin clean and free from dirt and bacteria. Make sure to remove any foreign objects, such as debris, dirt, or splinters, from the skin to prevent potential infections.
2. Proper wound care
Wounds and injuries are common gateways for bacterial infections leading to cellulitis. Promptly clean and treat any wounds or cuts your horse may have to prevent infection. Use a gentle antiseptic solution and dress the wound appropriately to promote healing and reduce the risk of bacterial infiltration.
3. Preventing skin injuries
Horses are prone to skin injuries, which can increase the risk of cellulitis. Taking preventive measures to minimize the occurrence of injuries is essential. Keep your horse’s environment free from sharp objects, provide adequate padding in stalls, and use protective gear such as boots or leg wraps during exercise or turnout to protect against accidental injuries.
4. Managing underlying conditions
Horses with pre-existing conditions like lymphedema, dermatitis, or other immune-suppressive disorders are more susceptible to cellulitis. Proper management of these underlying conditions is crucial to prevent cellulitis episodes. Consult with your veterinarian for appropriate treatment plans and guidelines.
5. Timely veterinary care
If you suspect your horse may have cellulitis or notice any symptoms such as heat, pain, swelling, or lameness, it is crucial to seek prompt veterinary care. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the progression of cellulitis and minimize the risk of complications. Follow your veterinarian’s recommendations for antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, pain management, and other necessary treatments.
6. Exercise and movement
Regular exercise and movement can help improve blood circulation and lymphatic drainage, reducing the risk of cellulitis in horses. Encourage regular exercise routines and turnout to promote overall health and reduce the chances of developing cellulitis.
7. Fly control
Flies can carry bacteria and increase the risk of skin infections in horses. Implement effective fly control measures, such as using fly repellents, fly masks, and keeping the stable and surrounding areas clean to reduce the attractiveness of the environment to flies.
8. Nutrition and immune support
A well-balanced diet, rich in nutrients and immune-supportive supplements, can help maintain a healthy immune system in horses. Adequate nutrition and immune support can enhance the body’s ability to fight off potential infections and reduce the likelihood of cellulitis.
In summary, preventing and managing cellulitis in horses involves maintaining good hygiene, proper wound care, preventing skin injuries, managing underlying conditions, seeking timely veterinary care, promoting exercise and movement, implementing fly control measures, and providing adequate nutrition and immune support. By following these strategies, horse owners can reduce the risk and severity of cellulitis and ensure the overall health and well-being of their horses.
Complications and Prognosis of Cellulitis in Horses
Cellulitis in horses can be a serious condition that can lead to various complications if left untreated. Understanding the potential complications and prognosis of cellulitis is important for horse owners and veterinarians.
1. Abscess Formation
One of the common complications of cellulitis in horses is the formation of abscesses. Abscesses can develop as a result of bacterial infection spreading deeper into the tissues. These abscesses can be painful and may require drainage and further treatment.
It is essential to monitor the affected area closely for any signs of abscess formation, such as increased pain, swelling, and the presence of pus. Early detection and appropriate treatment can help prevent further complications.
2. Lameness
Cellulitis can also lead to lameness in horses. The inflammation and swelling associated with cellulitis can affect the horse’s ability to move comfortably. Lameness may range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of cellulitis and the affected area.
Proper rest, pain management, and supportive care are crucial in managing lameness associated with cellulitis. In some cases, additional treatments such as physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications may be necessary to promote healing and alleviate discomfort.
3. Secondary Infections
Another concern with cellulitis in horses is the risk of secondary infections. The compromised skin barrier and underlying inflammation make the affected area more susceptible to the invasion of other bacteria or fungi.
Horse owners and veterinarians must closely monitor the cellulitis site for any signs of secondary infections, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge. Prompt treatment with appropriate antimicrobial agents is necessary to prevent the spread of infection and further complications.
4. Chronic Cellulitis
In some cases, cellulitis can become chronic, leading to long-term complications. Chronic cellulitis refers to recurring or persistent inflammation and infection in the affected area.
Chronic cellulitis may require more aggressive and prolonged treatment, including antibiotics, wound management, and close monitoring. It is important to address any underlying factors that may contribute to the development of chronic cellulitis, such as poor immune function or inadequate wound healing.
Prognosis of Cellulitis in Horses
The prognosis of cellulitis in horses can vary depending on various factors, including the severity of the infection, the promptness of treatment, and the overall health of the horse.
With timely and appropriate treatment, many cases of cellulitis in horses can be successfully managed, and the horse can recover without significant long-term consequences. However, more severe cases or those with complications may require more intensive treatment and have a longer recovery period.
It is important for horse owners to work closely with their veterinarian to develop an individualized treatment plan and ensure proper care and monitoring throughout the healing process.
Cellulitis in horses can lead to various complications, including abscess formation, lameness, secondary infections, and chronic cellulitis. Prompt and proper treatment is crucial in managing these complications and improving the prognosis for affected horses.
FAQs
What is cellulitis in horses?
Cellulitis in horses is a bacterial infection that affects the skin, tissues, and sometimes underlying structures. It is characterized by heat, pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area. Cellulitis can occur in any part of the horse’s body, but it is most commonly seen in the legs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cellulitis in horses is a serious condition that requires prompt veterinary attention. It is an inflammatory bacterial infection that affects the deeper layers of the horse’s skin and underlying connective tissues. Cellulitis can be caused by various factors such as wounds, scratches, or insect bites. The symptoms include heat, swelling, pain, and lameness in the affected area. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, including antibiotics and supportive care, are crucial for the successful management of cellulitis. Horse owners should practice good hygiene and regularly monitor their horse’s skin for any signs of infection to prevent the onset or spread of cellulitis.
Overall, cellulitis can significantly impact a horse’s well-being and performance if left untreated. Therefore, it is important to consult with a veterinarian as soon as symptoms are noticed. With proper care, attention, and timely treatment, horses can recover from cellulitis and return to their normal activities.
