If you’re fascinated by horses and want to deepen your understanding of their skeletal and muscular makeup, you’ve come to the right place. Studying horses and their anatomy is an engaging and enlightening journey into the world of these majestic creatures. By exploring their skeletal structure and muscular system, you’ll gain valuable insights into their movement, physiology, and overall health. In this guide, we’ll provide you with essential tips and resources to help you embark on your journey of studying horses and their fascinating skeletal and muscular makeup.

Understanding the Anatomy of Horses: A Comprehensive Guide
As an equestrian enthusiast, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the anatomy of horses. Knowing how a horse’s body is structured and functions can greatly contribute to their overall welfare, training, and performance. In this section, we will explore the different aspects of a horse’s anatomy, from their skeletal system to their muscular structure.
Skeletal System
The skeletal system forms the framework of a horse’s body. It provides support, protection, and enables movement. The bones of a horse are strong and durable, designed to withstand the rigors of their daily activities. Some key features of a horse’s skeletal system include:
- The skull: The horse’s skull protects the brain and houses important sensory organs such as the eyes, ears, and nose.
- The vertebral column: Composed of numerous vertebrae, the vertebral column provides flexibility and support to the horse’s body.
- The limbs: The limbs of a horse consist of the forelimbs and hindlimbs, each with their own set of bones and joints that enable locomotion.
- The hooves: The hooves play a critical role in the horse’s movement, providing traction and shock absorption.
Muscular System
The muscular system of a horse is responsible for generating movement and power. Horses possess well-developed muscles, allowing them to perform a variety of tasks with ease. Understanding the muscular system is crucial for training and conditioning purposes. Here are some key muscles found in a horse:
- The neck muscles: The neck muscles provide stability and flexibility to the horse’s head and neck.
- The shoulder muscles: The shoulder muscles are responsible for the horse’s forelimb movement.
- The back muscles: The back muscles support the rider’s weight and aid in maintaining balance.
- The hindquarter muscles: The hindquarter muscles are crucial for propulsion and power during activities such as jumping or running.
Respiratory System
The respiratory system of a horse is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Horses have highly efficient respiratory systems, enabling them to perform strenuous activities without fatigue. Here are some key components of a horse’s respiratory system:
- The nostrils: Horses have large and mobile nostrils that allow for increased airflow during exercise.
- The trachea: The trachea, or windpipe, connects the nostrils to the lungs, facilitating the passage of air.
- The lungs: The lungs are responsible for oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide.
- The diaphragm: The diaphragm is a large muscle that aids in the inhalation and exhalation process.
Digestive System
The digestive system of a horse is designed to process and extract nutrients from a primarily plant-based diet. Understanding the digestive system is crucial for proper feeding and nutrition management. Some key components of a horse’s digestive system include:
- The mouth: Horses have specialized teeth and a complex jaw structure that aids in the grinding and chewing of food.
- The esophagus: The esophagus transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
- The stomach: The stomach plays a key role in the initial breakdown of food through the secretion of gastric juices.
- The small and large intestines: These organs are responsible for the absorption of nutrients and water.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system of a horse is responsible for the transportation of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. It plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of the horse. Key components of the circulatory system include:
- The heart: The horse’s heart pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
- The arteries and veins: Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- The capillaries: Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that facilitate the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products at the cellular level.
Nervous System
The nervous system of a horse controls and coordinates all bodily functions, including movement, sensation, and behavior. Understanding the nervous system is fundamental for training
Essential Skeletal Structures of Horses: Learn the Basics
Understanding the skeletal structures of horses is essential for anyone interested in equine anatomy and horsemanship. The horse’s skeletal system provides support, protects vital organs, and enables movement. In this section, we will explore the key skeletal structures of horses and delve into their functions and significance.
The Skull
The skull of a horse is a complex structure that houses the brain and protects the sensory organs. It consists of various bones, including the frontal bone, parietal bone, occipital bone, and mandible. The skull’s shape and size play a crucial role in determining the horse’s facial profile.
The most prominent feature of the horse’s skull is the nasal bones, which form the bridge of the nose. The mandible, also known as the lower jaw, supports the horse’s teeth and allows for chewing and grinding of food.
The Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, commonly referred to as the backbone, extends from the skull to the tailbone. It is composed of multiple vertebrae, which are categorized into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and caudal.
The cervical vertebrae, located in the neck region, allow for the horse’s ability to flex, extend, and rotate its head. The thoracic vertebrae are attached to the ribs and provide support to the horse’s chest and back. The lumbar vertebrae are found in the lower back area and play a crucial role in facilitating the horse’s movement.
The sacral vertebrae connect the spine to the pelvis and contribute to the horse’s stability and balance. Finally, the caudal vertebrae, located in the tail region, provide support and flexibility to the horse’s tail.
The Limbs
The limbs of a horse are intricate structures that enable movement and support the horse’s body weight. Each limb consists of several bones, including the humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges in the forelimbs, and the femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges in the hindlimbs.
The limbs are divided into two main parts: the upper limb, which connects to the trunk, and the lower limb, which extends from the knee or hock to the hoof. The hooves, made of tough keratinized tissue, are vital for the horse’s locomotion and overall stability.
The Pelvis
The pelvis is a ring-like structure formed by the fusion of multiple bones. It connects the vertebral column to the hindlimbs and supports the weight of the horse’s body. The pelvis provides attachment points for the muscles and ligaments involved in locomotion and plays a crucial role in the horse’s overall stability and movement.
In Summary
Having a basic understanding of the essential skeletal structures of horses is vital for anyone involved in horse care, training, or veterinary medicine. The skull, vertebral column, limbs, and pelvis all contribute to the horse’s overall anatomy and functionality. By learning about these structures and their functions, you can better appreciate the complexity of the equine skeletal system and apply this knowledge to various aspects of horsemanship.
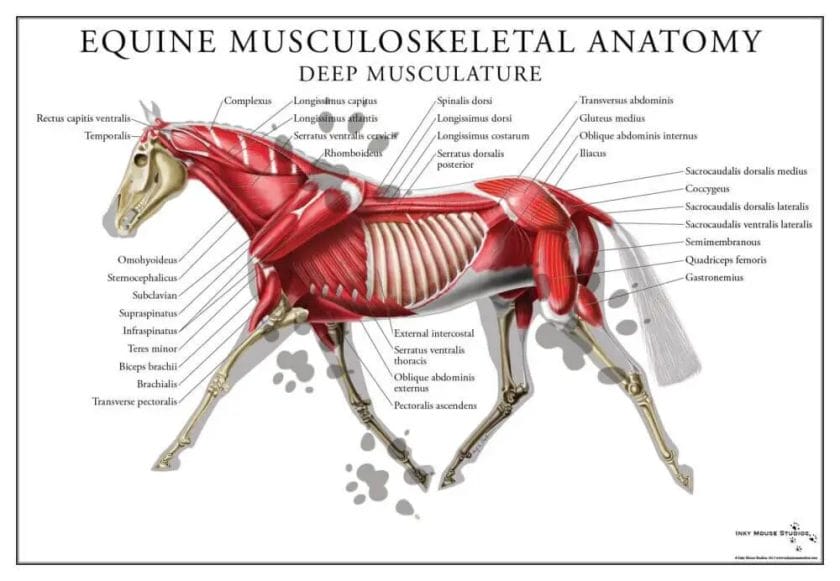
Unveiling the Muscular System of Horses: Key Components Revealed
Horses are magnificent creatures, known for their strength, agility, and grace. Behind their majestic appearance lies a complex and powerful muscular system that enables them to perform a wide range of tasks. In this section, we will explore the key components of the muscular system in horses and gain a deeper understanding of how these muscles contribute to their remarkable abilities.
Anatomy of Equine Muscles
The muscular system of a horse consists of various muscles that are responsible for movement, stability, and support. These muscles are categorized into different groups based on their location and function.
1. Superficial Muscles: These are the muscles that lie closer to the surface of the horse’s body. They are responsible for controlling the horse’s overall movement and provide the external appearance of the horse’s body shape. Superficial muscles include the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and gluteal muscles.
2. Deep Muscles: Deep muscles, as the name suggests, are located deeper within the horse’s body. They provide stability and support to the horse’s skeletal structure. These muscles include the pectoral muscles, longissimus dorsi, and quadriceps femoris.
3. Flexor and Extensor Muscles: Flexor muscles enable the bending of joints, while extensor muscles facilitate the extension of joints. These muscle groups work together to provide the horse with coordinated limb movement. Notable flexor and extensor muscles include the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, and gastrocnemius muscles.
Functions of Equine Muscles
The muscular system of horses plays a vital role in their ability to perform various activities. Let’s take a closer look at some key functions of these muscles:
1. Movement: The primary function of equine muscles is to provide locomotion. These muscles work in harmony to generate the force required for different gaits and movements, such as trotting, cantering, and galloping.
2. Balance and Stability: The muscles of a horse’s core and limbs work together to maintain balance and stability. Strong and well-developed muscles help the horse maintain a steady posture, especially during activities that require agility, such as jumping or navigating uneven terrain.
3. Strength and Power: Horses are known for their immense strength, and their muscles play a key role in generating power. Well-conditioned muscles enable horses to perform tasks that require significant force, such as pulling heavy loads or executing jumps with precision.
4. Endurance: Equine muscles are also responsible for providing the stamina required for prolonged physical activities. Muscles with good endurance enable horses to perform longer rides or participate in endurance competitions without fatigue.
Care and Conditioning of Equine Muscles
It is essential to provide proper care and conditioning to maintain the health and functionality of a horse’s muscular system. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Exercise: Regular exercise is crucial for developing and maintaining strong muscles in horses. A well-rounded exercise program that includes a variety of activities, such as riding, lunging, and turnout, helps keep the muscles toned and improves overall fitness.
2. Proper Nutrition: A balanced diet is essential for supporting muscle health in horses. Providing adequate amounts of protein, vitamins, and minerals ensures proper muscle development and repair.
3. Warm-up and Cool-down: Before and after any strenuous activity, it is important to warm up and cool down the horse’s muscles properly. Gentle stretching exercises and gradual warm-up routines help prevent muscle strain and promote flexibility.
4. Massage and Therapy: Massage and other forms of therapy, such as hydrotherapy or chiropractic care, can help relax and rehabilitate equine muscles. These therapies improve blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and enhance overall muscle function.
Summary
In summary, the muscular system of horses consists of various muscles that enable them to perform a wide range of tasks. Superficial and deep muscles, along with flexor and extensor muscles, work together to provide movement, stability, strength, and endurance. Proper care, including exercise, nutrition, warm-up and cool-down routines, and therapies, is essential for maintaining the health and functionality of a horse’s muscular system. By understanding the key components and functions of these muscles, we
Examining the Relationship Between Horse Skeleton and Muscle Function
In the field of equine anatomy and biomechanics, there is a fascinating relationship between the horse’s skeletal structure and its muscle function. Understanding how these two components work together is essential for horse owners, trainers, and veterinarians alike. In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of this relationship and explore the impact it has on a horse’s movement and overall performance.
Horse Skeleton: The Foundation of Movement
The horse’s skeleton serves as the framework that supports and protects its vital organs, muscles, and other tissues. Composed of bones, joints, and ligaments, the skeleton provides structural integrity and allows for a wide range of movement. It acts as the foundation upon which the horse’s musculature operates.
The horse’s skeleton is made up of approximately 205 bones, each with a specific shape and function. The long bones, such as the femur and humerus, provide leverage and support for the horse’s powerful muscles. The spine, consisting of vertebrae, enables flexibility while maintaining stability. Joints, such as the hock and knee, allow for movement and absorb shock during locomotion.
Muscle Function: Power and Precision
Horse muscles play a critical role in locomotion, stability, and overall performance. They work in tandem with the skeletal system to generate movement, absorb impact, and maintain balance. Muscles are responsible for both power and precision, enabling the horse to perform a wide array of tasks.
There are three types of muscles in horses: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscles, attached to bones via tendons, are responsible for voluntary movement. They contract and relax to produce force and generate motion. Cardiac muscles, found in the heart, ensure its continuous pumping action. Smooth muscles, present in various internal organs, regulate involuntary movements, such as digestion and breathing.
When a horse moves, its muscles undergo a complex sequence of contractions and relaxations. The coordinated action of agonist and antagonist muscles enables smooth and efficient movement. Agonist muscles contract to initiate a movement, while antagonist muscles relax to allow it to occur. This interplay of muscles ensures coordinated movement and minimizes the risk of injury.
The Interplay Between Skeleton and Muscles
The horse’s skeleton and muscles work collaboratively to create movement and maintain stability. The skeletal structure provides the attachment points for muscles, allowing for leverage and force generation. On the other hand, muscles exert tension on bones, creating joint movements and promoting locomotion.
As a horse moves, the contraction of muscles pulls on the skeletal system, causing bones to pivot and joints to flex or extend. This coordinated movement allows the horse to walk, trot, canter, gallop, and perform intricate maneuvers. The skeletal system, in turn, provides the necessary support and stability for muscle action.
The relationship between the horse’s skeleton and muscles is finely tuned. Any imbalance or dysfunction in either component can result in reduced performance or even injury. Proper conditioning, training, and a well-balanced diet are essential for maintaining the health and function of both the skeletal and muscular systems.
In summary, the relationship between a horse’s skeleton and muscle function is intricate and crucial for its overall performance. The skeletal system provides the framework for muscle attachment and movement, while muscles generate the force necessary for locomotion and stability. Understanding this interplay is vital for anyone involved in horse care and training. By optimizing the health and function of both the skeletal and muscular systems, horse owners and trainers can enhance their horse’s performance and ensure its well-being.
The Importance of Proper Horse Anatomy Knowledge for Training and Care
Proper horse anatomy knowledge is essential for anyone involved in the training and care of horses. Understanding the structure and function of a horse’s body not only helps in diagnosing and treating injuries and illnesses but also plays a vital role in training and maintaining the overall health and well-being of these magnificent creatures.
1. Recognizing signs of discomfort or injury: Having a thorough understanding of horse anatomy allows trainers and caretakers to identify signs of discomfort or injury more effectively. Horses cannot communicate their pain or discomfort in words, so it is essential to rely on their body language and physical responses. By knowing the location and function of various body parts, trainers and caretakers can quickly recognize any changes or abnormalities in the horse’s behavior or movement, indicating a potential issue.
2. Implementing proper training techniques: Horse anatomy knowledge is instrumental in developing effective training techniques. Each part of a horse’s body serves a specific purpose, and understanding how these parts work together allows trainers to develop exercises that strengthen the correct muscles and improve performance. For example, knowledge of the horse’s skeletal and muscular systems can help trainers design workouts that target specific areas, such as building hindquarter strength or improving flexibility in the neck and back.
3. Preventing injuries: By understanding the anatomy of a horse, trainers and caretakers can take proactive measures to prevent injuries. They can design exercise routines that minimize strain on vulnerable areas and ensure proper warm-up and cool-down routines to prevent muscle stiffness. Furthermore, knowledge of the horse’s skeletal structure can help trainers assess the suitability of certain activities or equipment, avoiding potential damage or discomfort for the horse.
4. Administering appropriate healthcare: Proper horse anatomy knowledge is crucial when it comes to administering healthcare. Whether it’s applying bandages, administering medications, or performing routine health checks, understanding the underlying anatomy ensures that these tasks are carried out correctly and safely. It allows caretakers to handle horses with precision, minimizing the risk of further injury or complications.
5. Communicating effectively with veterinarians: Horse owners and trainers often need to collaborate with veterinarians to address any health concerns or injuries. Having a solid understanding of horse anatomy enables effective communication with veterinarians. It allows for clearer descriptions of symptoms or areas of concern, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
6. Developing a deep bond: Finally, having knowledge of horse anatomy can deepen the bond between the horse and its caretaker. By understanding how the horse’s body works and the importance of proper training and care, individuals can provide the necessary support, comfort, and attention that promotes the horse’s overall well-being. This understanding fosters trust and a stronger connection between the horse and its handler.
In summary, proper horse anatomy knowledge is vital for successful training and care. It allows trainers and caretakers to recognize signs of discomfort or injury, implement effective training techniques, prevent injuries, administer appropriate healthcare, communicate effectively with veterinarians, and develop a deep bond with the horse. By prioritizing this knowledge, individuals can ensure the well-being and longevity of these incredible animals.
FAQs
1. How can I study the skeletal and muscular makeup of horses?
To study the skeletal and muscular makeup of horses, you can start by reading books and resources on equine anatomy. Additionally, attending workshops, seminars, or online courses specifically focused on equine anatomy can provide hands-on learning opportunities. Utilizing anatomical charts, models, and dissection tutorials can also enhance your understanding.
2. What are some recommended resources for studying horse anatomy?
Some recommended resources for studying horse anatomy include books like “Equine Anatomy: A Guide for Artists” by Eleanor Kish, “Horse Anatomy: A Coloring Atlas” by Robert A. Kainer and Thomas O. McCracken, and “Horse Anatomy: A Pictorial Approach to Equine Structure” by Peter C. Goody.
3. Are there any online resources or apps available for studying horse anatomy?
Yes, there are several online resources and apps available for studying horse anatomy. Some popular ones include Equine Anatomy 3D, Horse Anatomy: Equine 3D, and Anatomy of the Horse – An Illustrated Guide.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, studying horses and their skeletal and muscular makeup is an essential aspect of understanding their anatomy and physiology. By delving into the intricate details of their bones, muscles, and connective tissues, researchers, veterinarians, and horse enthusiasts gain valuable insights into their locomotion, performance, and overall well-being. Moreover, this knowledge plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating equine injuries, improving training techniques, and enhancing the overall health and welfare of horses.
Exploring the skeletal and muscular systems of horses allows us to appreciate the remarkable adaptability and athletic capabilities of these magnificent creatures. By examining the structure and function of their bones, we gain a deeper understanding of their ability to support their weight and withstand the rigors of various equestrian disciplines.
Additionally, studying their muscles helps us comprehend how they generate power, produce movement, and maintain balance during different gaits and activities.
By continuously advancing our knowledge in this field, we can ensure better horse management practices, promote their well-being, and contribute to the development of innovative therapies and training methods for these incredible animals.
In summary, studying the skeletal and muscular makeup of horses is not only fascinating but also essential for their optimal care and performance.
