Stringhalt in horses is a neurologic disorder that causes involuntary leg movements, sometimes making it difficult for them to walk or perform certain tasks. While there is no specific cure for stringhalt, various treatment options can help manage the condition and improve the horse’s quality of life. Physical therapy, medication, and dietary changes are among the approaches used to alleviate symptoms. It is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to develop a personalized treatment plan for a horse affected by stringhalt.
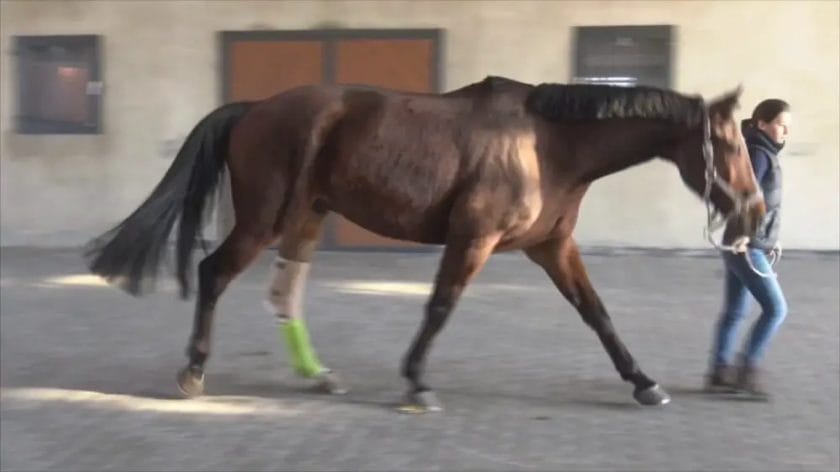

Common Symptoms and Diagnosis of Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a neuromuscular disorder that affects horses, causing abnormal movements in the hind legs. It is characterized by exaggerated flexion of the hind limbs, often accompanied by a sudden, jerking motion. These movements can be distressing for both the horse and the owner, and it is important to recognize the common symptoms of stringhalt in order to seek appropriate veterinary care.
Symptoms
The most noticeable symptom of stringhalt in horses is the exaggerated flexion of the hind legs. This can be observed when the horse takes a step forward, as one or both hind legs will jerk upward in a rapid, involuntary motion. The affected leg may also be held up for a longer period of time than usual, causing the horse to appear unsteady or hesitant when walking. In severe cases, the horse may have difficulty walking or even experience episodes of falling.
In addition to these characteristic movements, horses with stringhalt may exhibit other symptoms such as muscle stiffness, muscle atrophy, and a shortened stride. They may also show signs of pain, such as flinching or reacting negatively when the affected leg is palpated or manipulated.
Diagnosis
If you suspect that your horse has stringhalt, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis. The vet will begin by conducting a thorough physical examination and medical history review. They may ask you questions about the horse’s symptoms, duration, and any potential triggers or changes in behavior.
One of the primary diagnostic tools for stringhalt is a flexion test. This involves flexing the horse’s hind limb for a short period of time and then releasing it to observe the response. Horses with stringhalt will typically exhibit the characteristic jerking motion when the leg is released from flexion.
X-rays or ultrasound imaging may also be used to assess the condition of the horse’s muscles and nerves. This can help to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms and provide more information about the underlying cause of the stringhalt.
In some cases, additional diagnostic tests such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies may be recommended to evaluate the electrical activity and function of the affected muscles and nerves.
Summary
Stringhalt in horses is a neuromuscular disorder characterized by exaggerated flexion of the hind legs. Common symptoms include the jerking motion of the hind limbs, muscle stiffness, and a shortened stride. Diagnosis involves a thorough physical examination, flexion tests, imaging studies, and sometimes specialized tests to evaluate muscle and nerve function. If you suspect your horse has stringhalt, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
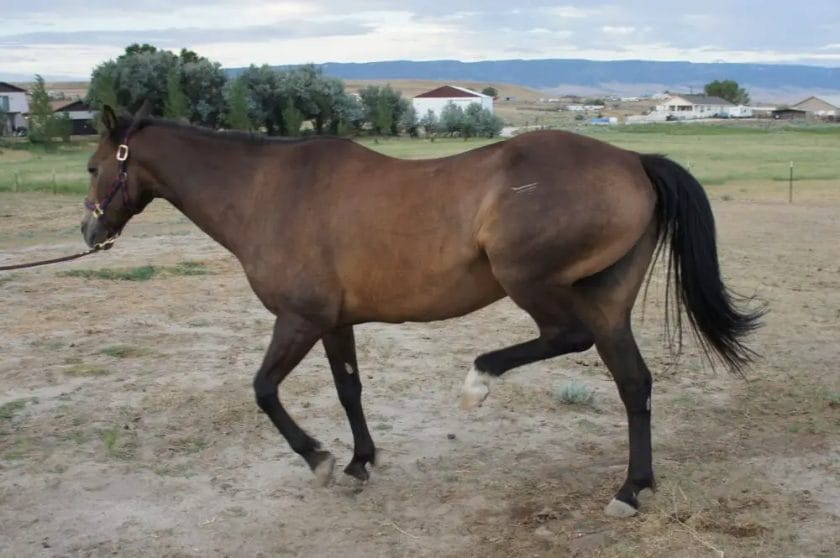

Treatment Options for Stringhalt in Horses
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses and is characterized by involuntary and exaggerated movements of the hind legs. It can cause a horse to lift its leg excessively high or jerk it back suddenly. Stringhalt can be both a temporary or a chronic condition, and it can significantly impact a horse’s gait and overall performance. If your horse is diagnosed with stringhalt, it’s important to explore the treatment options available to help manage the condition.
1. Rest and Rehabilitation
For mild cases of stringhalt, rest and rehabilitation may be the primary treatment approach. Giving the affected horse ample time to rest and recover can help reduce symptoms and allow the horse to regain normal mobility. Restricting exercise and providing a safe and comfortable environment can aid in the healing process.
2. Medications
In more severe cases of stringhalt, medications may be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms and improve the horse’s quality of life. Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Muscle relaxants may also be used to help relax the affected muscles and reduce the severity of the involuntary movements.
3. Surgical Intervention
In certain instances, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat stringhalt. Surgical procedures such as tenotomy or myectomy aim to release or remove the affected muscle or tendon, reducing the severity of the condition. These procedures are typically reserved for severe cases of stringhalt that do not respond well to other treatment options.
4. Alternative Therapies
Some horse owners may choose to explore alternative therapies as complementary treatments for stringhalt. These therapies may include acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, or physical therapy. While the effectiveness of these treatments may vary, they can be used in combination with traditional treatment options to help manage the symptoms of stringhalt.
5. Dietary Changes
In certain cases, dietary changes may be recommended to support the overall health and well-being of a horse with stringhalt. Ensuring a balanced diet that meets the nutritional needs of the horse can help support their overall immune system and promote healing. Consultation with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist can help determine the best dietary plan for a horse with stringhalt.
6. Management Techniques
Managing a horse with stringhalt involves implementing certain techniques to minimize stress and reduce the risk of exacerbating symptoms. This includes providing a well-maintained and obstacle-free environment, avoiding activities that may trigger symptoms, and maintaining regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the horse’s condition.
7. Long-term Care and Monitoring
Stringhalt is a chronic condition, and long-term care and monitoring are necessary to ensure the well-being of the affected horse. Regular veterinary check-ups, ongoing management techniques, and adjustments to treatment plans may be required to address any changes in the horse’s condition over time.
Summary
Stringhalt in horses can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right treatment approach, it is possible to improve the horse’s quality of life. Treatment options for stringhalt include rest and rehabilitation, medications, surgical intervention, alternative therapies, dietary changes, management techniques, and long-term care and monitoring. It’s important to work closely with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable treatment plan for an individual horse, taking into consideration the severity of the condition and the horse’s overall health.
Rehabilitation and Management Strategies for Horses with Stringhalt
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses, causing them to exhibit exaggerated and uncontrolled movements in their hind legs. It can be a result of various factors such as nerve damage, trauma, or nutritional deficiencies. While there is currently no known cure for stringhalt, there are several rehabilitation and management strategies that can help improve the quality of life for horses suffering from this condition.
1. Veterinary Assessment and Diagnosis
The first step in managing stringhalt is to seek professional veterinary assessment and diagnosis. A veterinarian will perform a thorough examination, including physical and neurological assessments, to determine the severity of the condition and rule out any underlying causes. This is crucial in developing an effective rehabilitation and management plan tailored to the individual horse’s needs.
2. Continued Veterinary Monitoring
Once the initial assessment is done, ongoing veterinary monitoring is essential to track the progress of the horse’s condition. Regular check-ups will help identify any changes or complications that may arise, allowing for prompt intervention and adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary.
3. Exercise and Physical Therapy
Exercise and physical therapy play a vital role in the rehabilitation of horses with stringhalt. Controlled movement and conditioning exercises can help improve muscle strength, coordination, and flexibility in the affected limbs. It is important to consult with a professional equine therapist to develop a customized exercise program that gradually increases in intensity and duration, while taking into consideration the horse’s individual capabilities and limitations.
4. Nutritional Management
Proper nutrition is key to supporting the overall health and well-being of horses with stringhalt. A well-balanced diet that meets the horse’s specific nutritional requirements, including essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins, can aid in the recovery process and prevent further complications. It is advisable to consult with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to develop a suitable feeding plan tailored to the horse’s needs.
5. Environmental Modifications
Modifications to the horse’s environment can help minimize the risk of injury and provide a safer living space. This may include ensuring proper footing in the horse’s living and exercise areas, eliminating any hazards or obstacles that may exacerbate the symptoms of stringhalt, and providing ample space for the horse to move comfortably without restriction.
6. Medications and Supplements
In some cases, veterinarians may prescribe medications or recommend supplements to manage the symptoms of stringhalt. These may include anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and inflammation, muscle relaxants to alleviate muscle spasms, or supplements that support nerve health. It is important to follow the veterinarian’s guidance regarding medication administration and dosage.
7. Farrier and Hoof Care
Regular farrier visits and proper hoof care are essential for horses with stringhalt. A skilled farrier can address any hoof imbalances or abnormalities that may contribute to the horse’s discomfort and instability. Corrective shoeing or trimming techniques can provide support and enhance the horse’s overall balance and movement.
8. Emotional Support and Management
Horses with stringhalt may experience emotional distress due to their condition. Providing a calm and stress-free environment, along with social interactions and mental stimulation, can help improve their overall well-being. Additionally, practicing patience and understanding during training and handling sessions can help build trust and confidence, reducing anxiety and promoting a positive mindset.
In summary, while there is no cure for stringhalt, a comprehensive approach that combines veterinary care, exercise, nutrition, environmental modifications, and emotional support can greatly improve the quality of life for horses affected by this condition. It is important to work closely with a veterinarian and other equine professionals to develop an individualized rehabilitation and management plan that addresses the specific needs of each horse.
Preventing Stringhalt in Horses: Tips and Best Practices
Stringhalt is a condition that affects horses, causing abnormal movements in their hind legs. The exact cause of stringhalt is still unknown, but it is believed to be related to nerve damage or dysfunction. This condition can greatly affect a horse’s mobility and overall well-being. Fortunately, there are several tips and best practices that can help prevent stringhalt in horses.
1. Provide a Nutritious Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for maintaining the overall health of horses. Ensuring that your horse’s diet is rich in essential vitamins and minerals can help support their nerve health and prevent conditions like stringhalt. Consult with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to formulate a diet plan that meets your horse’s specific nutritional needs.
2. Regular Exercise and Turnout
Regular exercise and turnout are not only beneficial for a horse’s physical well-being but also for their mental health. Allowing your horse ample time to move around and stretch their muscles can help prevent muscle stiffness and nerve damage, which may contribute to the development of stringhalt. Aim for at least a few hours of turnout each day, allowing your horse to graze and move about freely.
3. Proper Hoof Care
Proper hoof care is crucial for a horse’s overall health and soundness. Regular trimming and maintenance of the hooves can help prevent imbalances and issues with the horse’s gait that may contribute to stringhalt. Work with a skilled farrier to ensure that your horse’s hooves are in optimal condition.
4. Minimize Stress and Anxiety
Horses are sensitive animals and can easily experience stress and anxiety, which may have an impact on their nervous system. Minimize stressful situations and provide a calm and consistent environment for your horse. This can include avoiding sudden changes in routine, providing adequate socialization, and ensuring a comfortable living space.
5. Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for monitoring your horse’s overall health and addressing any potential issues early on. A veterinarian can assess your horse’s neurological health and provide appropriate treatment or recommendations to prevent the development or progression of stringhalt.
6. Avoid Toxic Substances
Some plants, chemicals, and substances can be toxic to horses and may contribute to nerve damage or dysfunction. Familiarize yourself with common toxic plants in your area and ensure that your horse’s grazing areas are free from these plants. Additionally, be cautious with any medications, chemicals, or feed additives that may have adverse effects on your horse’s nervous system.
7. Genetic Considerations
While it may not be possible to prevent stringhalt in horses with a genetic predisposition, understanding the horse’s lineage and any potential genetic factors can be helpful in managing the condition. If possible, obtain a detailed history of the horse and its lineage to identify any patterns of stringhalt.
8. Consult with a Professional
If you suspect that your horse may be at risk for developing stringhalt or exhibits symptoms of the condition, it is important to consult with a professional. A veterinarian or equine specialist can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and offer guidance on preventing stringhalt.
Summary
Preventing stringhalt in horses requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses proper nutrition, regular exercise and turnout, proper hoof care, stress reduction, regular veterinary check-ups, avoidance of toxic substances, genetic considerations, and professional guidance. By following these tips and best practices, horse owners can minimize the risk of their horses developing stringhalt and ensure their overall well-being and mobility.
FAQs
Can stringhalt in horses be cured?
Stringhalt in horses is a neurological condition that causes involuntary upward movements of the hind legs. Unfortunately, there is currently no known cure for stringhalt. However, management techniques such as exercise, changing the horse’s diet, and specific shoeing techniques can help minimize the symptoms and improve the horse’s quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stringhalt in horses is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on their overall well-being. While there is no definitive cure for stringhalt, there are several treatment options available to manage the symptoms and improve the horse’s quality of life. These may include dietary changes, exercise modifications, and the use of certain medications. Additionally, it is crucial to work closely with a veterinarian to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the horse’s specific needs. Although a complete cure may not be possible, proactive management and regular veterinary care can help alleviate the symptoms and ensure the horse’s comfort and happiness.
