Horses can indeed die from heaves, a chronic respiratory condition also known as equine asthma. Heaves is characterized by difficulty breathing, coughing, and excessive mucus production. If left untreated or poorly managed, it can lead to severe complications and even death. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for heaves is crucial in ensuring the health and well-being of horses.
While heaves can be a life-threatening condition, early detection and proper management can significantly improve the horse’s quality of life and increase their chances of survival. Maintaining a clean and dust-free environment, providing good ventilation, and implementing dietary changes are essential in managing heaves. Regular veterinary care and medication are also crucial in controlling the disease progression and preventing fatal outcomes.
Owners should always be vigilant for signs of respiratory distress in their horses and consult a veterinarian promptly if any abnormalities are observed. With proper care and management, horses with heaves can lead relatively normal lives and have a reduced risk of complications and fatality.

Identifying the Symptoms of Heaves in Horses: What to Look Out For
Heaves, also known as recurrent airway obstruction (RAO), is a common respiratory condition found in horses. It is similar to asthma in humans and can significantly impact a horse’s health and performance. Early identification of heaves symptoms is crucial for timely treatment and management. In this section, we will discuss the key symptoms to look out for when suspecting heaves in horses.
1. Coughing
One of the primary symptoms of heaves in horses is persistent coughing. The cough may be dry or accompanied by the production of thick mucus. Initially, the cough may only occur during or after exercise, but as the condition progresses, it may become more frequent and persistent.
2. Labored Breathing
Horses with heaves often exhibit labored breathing, especially during physical exertion or in dusty environments. You may notice increased effort during inhalation and exhalation, with visible flaring of the nostrils and heaving movement of the abdomen. In severe cases, even normal breathing at rest may become difficult for the affected horse.
3. Wheezing
Wheezing is another common symptom of heaves in horses. It is characterized by a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing, resulting from the narrowing of airways and obstruction of airflow. The wheezing may be more pronounced during expiration.
4. Nasal Discharge
If a horse has heaves, you may notice the presence of nasal discharge. The discharge is usually thick, sticky, and may be yellowish or greenish in color. This is a result of the inflammation and excessive mucus production in the airways.
5. Exercise Intolerance
Horses with heaves may display reduced exercise tolerance. They may tire more quickly, show signs of fatigue, and have difficulty maintaining their usual performance levels. This is due to the compromised respiratory function and the reduced ability to deliver oxygen to the muscles.
6. Weight Loss
Chronic respiratory conditions like heaves can lead to weight loss in horses. The increased effort required for breathing and reduced appetite due to discomfort may result in a gradual decline in body condition. It is important to monitor the horse’s weight regularly and consult with a veterinarian if significant weight loss occurs.
7. Allergic Reactions
Heaves is often triggered or exacerbated by allergens such as dust, mold spores, and pollen. Horses with heaves may display allergic reactions, including skin itchiness, hives, and swelling. These reactions are a result of the immune system’s response to allergens and the release of inflammatory mediators.
In summary, recognizing the symptoms of heaves in horses is essential in ensuring early intervention and effective management of the condition. If you observe persistent coughing, labored breathing, wheezing, nasal discharge, exercise intolerance, weight loss, or allergic reactions in your horse, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

Managing Heaves: Effective Treatment Options for Horses with Respiratory Issues
Heaves, also known as recurrent airway obstruction (RAO) or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), is a common respiratory condition in horses. It is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing and coughing. While there is no cure for heaves, with proper management and treatment, horses can lead a comfortable life. In this section, we will discuss effective treatment options for horses with respiratory issues.
1. Environmental Management
One of the key aspects of managing heaves is creating a suitable environment for the horse. This involves minimizing exposure to triggers such as dust, mold, and allergens. Some steps that can be taken include:
- Stable Design: Providing a well-ventilated stable with good airflow can help reduce the presence of irritants in the horse’s environment.
- Pasture Turnout: Allowing the horse to spend time in a pasture with clean air can help improve respiratory health.
- Dust Control: Using dust-free bedding, wetting hay before feeding, and keeping the stable clean can help minimize dust and allergen exposure.
- Ample Fresh Air: Ensuring the horse has access to fresh air by providing open windows or doors can aid in reducing respiratory symptoms.
2. Medications
Various medications can be used to manage heaves and alleviate symptoms. These medications work in different ways to help reduce inflammation, relax airway muscles, and improve breathing. The most common medications include:
- Bronchodilators: These medications help relax the muscles surrounding the airways, allowing for easier breathing. Examples include albuterol and clenbuterol.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications help reduce airway inflammation and swelling. They can be administered orally, by inhalation, or via injection.
- Anti-inflammatories: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as flunixin meglumine can help alleviate inflammation and pain associated with heaves.
3. Nutritional Management
Diet plays a crucial role in managing horses with heaves. Certain dietary adjustments can help support respiratory health and reduce symptoms. Consider the following:
- Low-Dust Forage: Feeding low-dust hay or hay alternatives, such as soaked hay or hay cubes, can help minimize respiratory irritants.
- Soaking Hay: Soaking hay for 30 minutes to an hour can help reduce dust and allergen levels.
- Grain Feeding: Reducing or eliminating grain intake can help prevent excess weight gain, which can worsen respiratory symptoms.
- Supplements: Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, can help support respiratory health.
4. Exercise and Weight Management
Regular exercise and weight management are important for horses with heaves. Exercise helps improve respiratory function and strengthen the respiratory muscles. It is important to gradually introduce exercise and avoid strenuous activities that may trigger respiratory distress.
Weight management is also essential, as excess weight can make breathing more difficult for horses with respiratory issues. A balanced diet, portion control, and regular monitoring of the horse’s weight can help maintain a healthy body condition.
5. Veterinary Care and Monitoring
Regular veterinary care is essential for horses with heaves. A veterinarian can provide proper diagnosis, monitor the horse’s condition, and adjust the treatment plan as needed. It is important to follow up with veterinary visits and communicate any changes or concerns regarding the horse’s respiratory health.
In summary, managing heaves in horses requires a comprehensive approach. Environmental management, medications, nutritional adjustments, exercise, weight management, and regular veterinary care are key components of an effective treatment plan. By implementing these strategies, horse owners can help their equine companions lead a comfortable and healthy life despite respiratory issues.
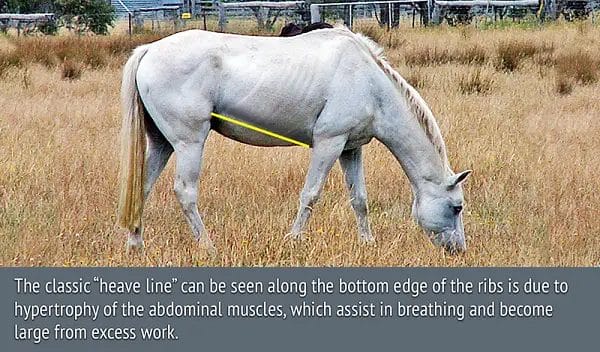
Preventing Heaves: Steps to Minimize the Risk and Improve Horse Health
Horses are majestic creatures that require proper care and attention to ensure their well-being. One common respiratory condition that can affect horses is called heaves. Heaves, also known as recurrent airway obstruction (RAO), is a chronic condition similar to asthma in humans. It can cause discomfort, difficulty breathing, and decreased performance in horses. However, with the right preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of heaves and improve the overall health of your horse.
1. Provide Good Ventilation
Proper ventilation is vital for maintaining a healthy environment for your horse. Make sure the barn or stable is well-ventilated with ample fresh air circulation. Avoid using dusty bedding or storing hay in the same area as the horses, as these can contribute to respiratory issues. Regularly clean the stable to remove any accumulated dust or mold.
2. Minimize Dust Exposure
Dust is a major trigger for heaves in horses. Take steps to minimize dust exposure by using low-dust bedding options, such as wood shavings or straw that has been properly cleaned and moistened. Avoid using dusty or moldy hay and opt for high-quality hay that is free from dust and mold spores.
If your horse is sensitive to dust, consider using a hay steamer to reduce airborne particles. Soaking hay in water before feeding can also help minimize dust inhalation.
3. Implement Proper Feeding Practices
Diet plays a crucial role in managing and preventing heaves. Feed your horse low-dust hay and consider providing hay in small-hole hay nets to slow down consumption and reduce dust inhalation.
Avoid feeding your horse directly from the ground, as this can increase exposure to dust and allergens. Instead, use elevated feeders to minimize dust contact.
4. Manage Pasture Access
Allowing your horse access to pasture is essential for their overall well-being. However, for horses prone to heaves, it’s important to manage pasture access carefully. Avoid turning horses out during peak pollen times, typically in the early mornings and late evenings. Consider using grazing muzzles to limit grass intake and reduce exposure to allergens.
5. Regular Exercise and Turnout
Regular exercise and turnout are crucial for maintaining proper respiratory function in horses. Exercise helps strengthen the lungs and improves overall cardiovascular fitness. Aim for daily turnout in a clean and dust-free paddock or pasture. Ensure the area is free from moldy or dusty vegetation.
6. Consult with a Veterinarian
If you suspect your horse may be at risk of developing heaves or if they are already showing symptoms, consult with a veterinarian. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend a customized management plan for your horse. This may include medication, such as bronchodilators or corticosteroids, to alleviate symptoms and manage the condition.
In summary, preventing heaves in horses requires proactive measures to minimize dust exposure, provide good ventilation, and manage diet and pasture access. By implementing these steps and working closely with a veterinarian, you can help minimize the risk of heaves and improve the overall respiratory health of your horse.
Supporting Horses with Heaves: Care and Supportive Measures for Affected Equines
Horses with heaves, also known as recurrent airway obstruction (RAO) or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), require special care and support to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Heaves is a respiratory condition that can cause coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing in affected horses. It is often triggered by allergens in the environment, such as dust, mold, or pollen.
If your horse has been diagnosed with heaves, it is important to work closely with your veterinarian to develop a comprehensive management plan. This plan may include medications, environmental modifications, and supportive measures to help alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Medications
There are several medications that can be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of heaves in horses. These may include bronchodilators, which help to relax the airway muscles and improve airflow, and corticosteroids, which reduce inflammation in the respiratory system. Your veterinarian will determine the appropriate medications and dosages for your horse based on its individual needs.
Environmental Modifications
Modifying your horse’s environment can play a significant role in managing heaves. Here are some helpful measures to consider:
- Stable Management: Ensure the stable is well-ventilated and free from dust and allergens. Regularly clean and dampen the bedding to minimize airborne irritants. Avoid using straw bedding, as it can harbor mold spores.
- Pasture Management: Provide ample turnout time in a clean and dust-free pasture. Avoid turning your horse out during high pollen or mold spore counts, which can trigger flare-ups. Consider using a grazing muzzle to limit the intake of allergens.
- Hay: Soak the hay in water for 30 minutes before feeding to minimize dust inhalation. Alternatively, consider feeding your horse haylage or steamed hay, which have lower dust levels.
- Feed: Choose low-dust feeds and avoid dusty or moldy feed ingredients. Provide fresh, clean water at all times.
Supportive Measures
In addition to medication and environmental modifications, there are supportive measures that can help manage heaves in horses:
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve respiratory function in horses with heaves. However, avoid exercising your horse in dusty or moldy environments, and monitor its breathing closely during exercise.
- Supplements: Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, may help reduce inflammation and support respiratory health. Consult with your veterinarian before adding any supplements to your horse’s diet.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for horses with heaves. Excess weight can put additional strain on the respiratory system. Consult with your veterinarian to ensure your horse’s diet is appropriate for its condition and body condition score.
Remember to work closely with your veterinarian and follow their recommendations for managing heaves in your horse. By implementing a comprehensive management plan, you can help alleviate symptoms, reduce the frequency of flare-ups, and improve your horse’s overall well-being.
FAQs
Can a horse die from heaves?
Yes, severe cases of heaves, also known as recurrent airway obstruction, can lead to a horse’s death if left untreated. The condition causes inflammation and constriction of the airways, making it difficult for the horse to breathe properly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while heaves can be a debilitating condition for horses, it is not typically a life-threatening ailment. With proper management and treatment, horses can live relatively normal lives despite the challenges posed by heaves. By implementing dietary changes, providing dust-free environments, and administering prescribed medications, horse owners can effectively control the symptoms and improve the respiratory health of their equine companions. It is important to closely monitor the horse’s condition and seek veterinary guidance to ensure the best possible outcome. Remember to consult with a veterinarian for a comprehensive understanding of heaves and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
